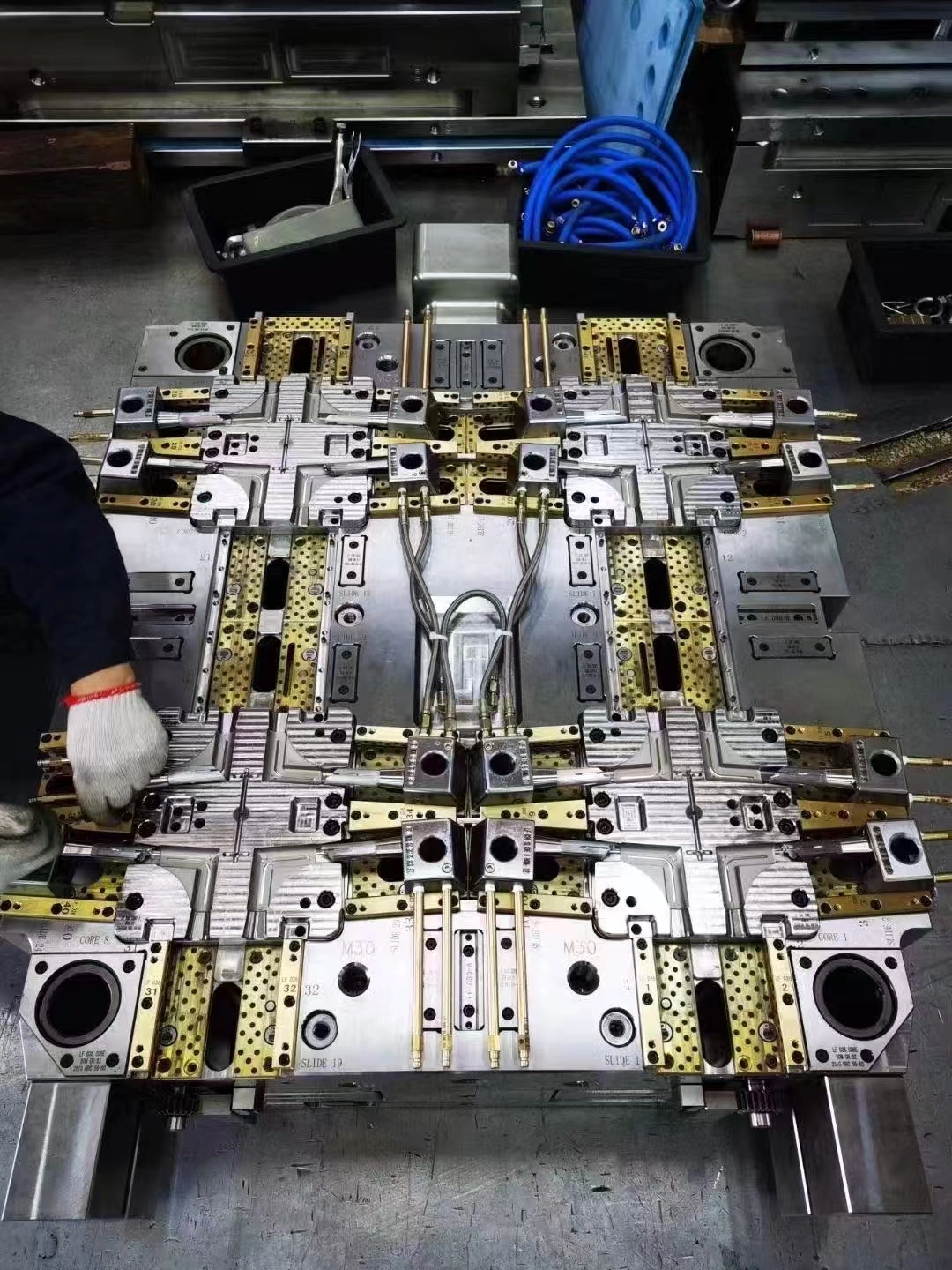
Glass-Filled Plastic Components for Structural Applications
Glass-filled plastic components are a big step forward in material engineering because they combine the flexibility of polymers with the strength of glass fiber support. These composite materials meet the rising need in the technology, automobile, consumer goods, and building industries for solutions that are strong but not too heavy. By adding glass strands to thermoplastic matrices, makers can make parts that are better at supporting weight than regular plastics while still being cheaper than metal options. Product makers and buying managers can make smart choices about where to get these specialized materials that meet performance needs and price limits if they know about their features, how they are made, and how to buy them.

Understanding Glass-Filled Plastic Components
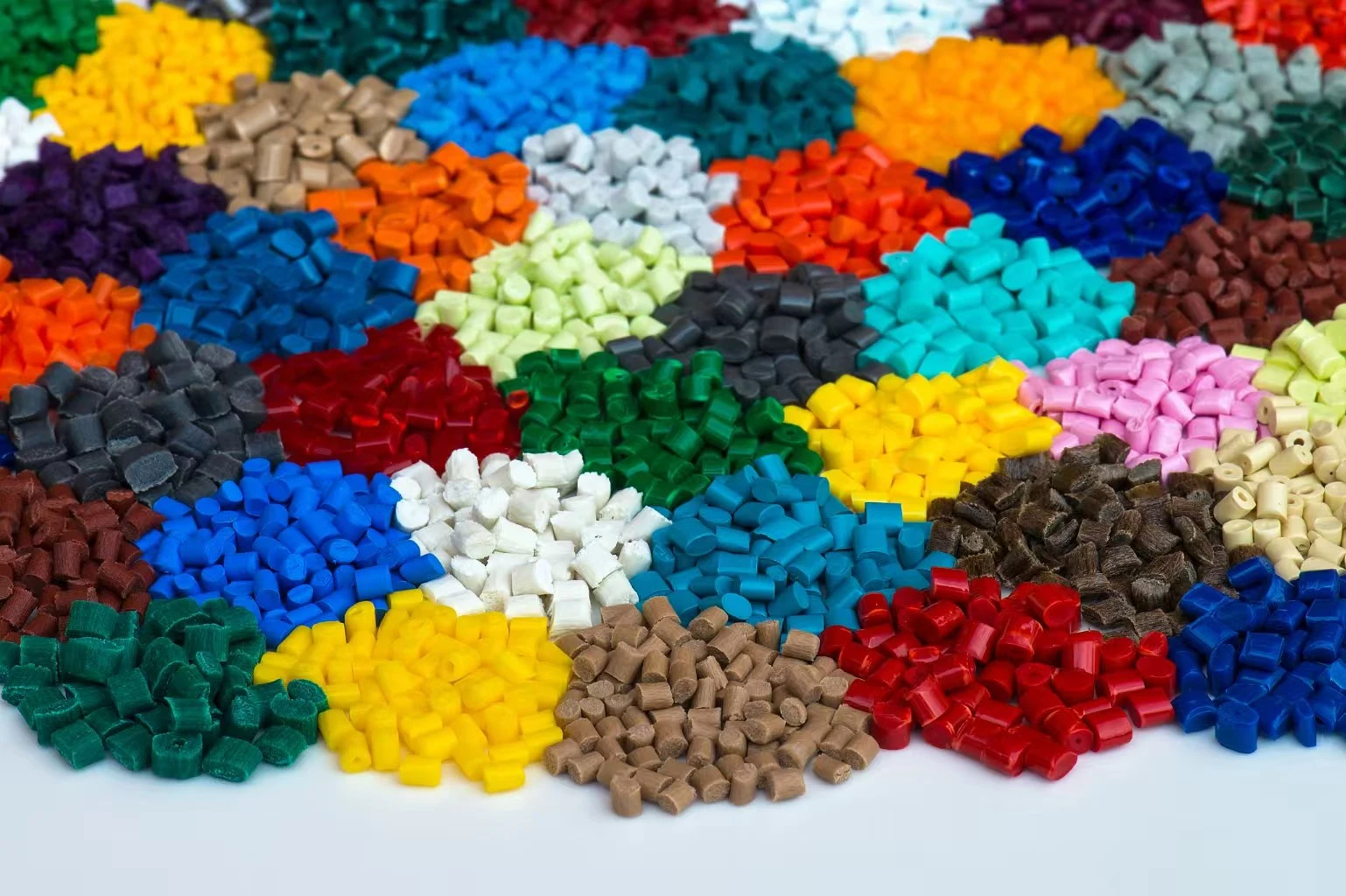
When we talk about cutting-edge industrial materials, glass-filled composites really stand out as a big deal for modern industry. These unique materials are made up of polymer bases and carefully measured glass fiber additions that work together to make parts that have great mechanical performance. The change happens at the molecular level, where glass strands (usually between 10 and 50 percent by weight) mix with the polymer material during processing.
Material Composition and Core Benefits
Terephthalate (PBT), or Polypropylene (PP) are often used as the main material in these mixtures. Each material gives the final part its own special properties. Nylon-based composites are great for jobs that need to be tough and resistant to chemicals, while PBT types are better at keeping their shape and insulating electricity. Polypropylene mixtures are very cost-effective for large-scale production runs. Adding glass fiber support greatly improves a number of important qualities. Tensile strength goes up by 200 to 300 percent compared to plastics that aren't filled, and bending stiffness goes up by as much as 400 percent. In the real world, these improvements to the mechanics directly lead to better results. Components can handle higher loads without deforming, keep their exact sizes even when temperatures change, and don't creep when under long-term stress. The heat displacement temperature of the material usually goes up by 40 to 80°C, which lets it be used in places where regular plastics would break.
Applications Across Industries
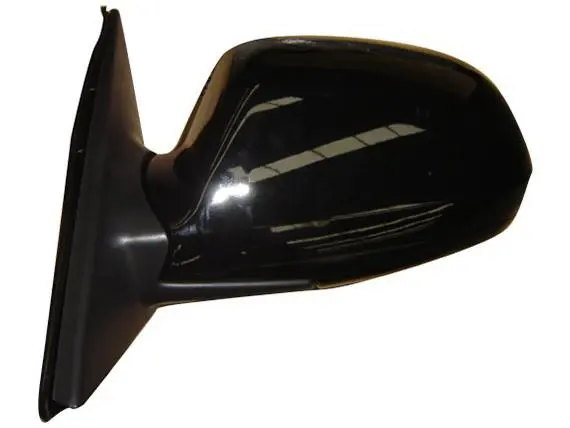
In the making of cars, metal parts are being replaced with glass-filled parts in engine spaces, transmission systems, and structural frames. Electronics companies use these materials to make equipment cases, connector housings, and circuit board supports that need to be strong and able to keep electricity out. They are used in power tool housings, appliance parts, and sports equipment where reliability and good looks are important. Parts like gear systems, mounting frames, and industrial screws are especially useful in the hardware industry. These parts are resistant to wear, which makes products last longer and requires less upkeep. The Society of Plastics Engineers did a study that showed glass-filled parts that are properly made can last more than ten years in harsh industrial settings.
Manufacturing Processes and Design Considerations
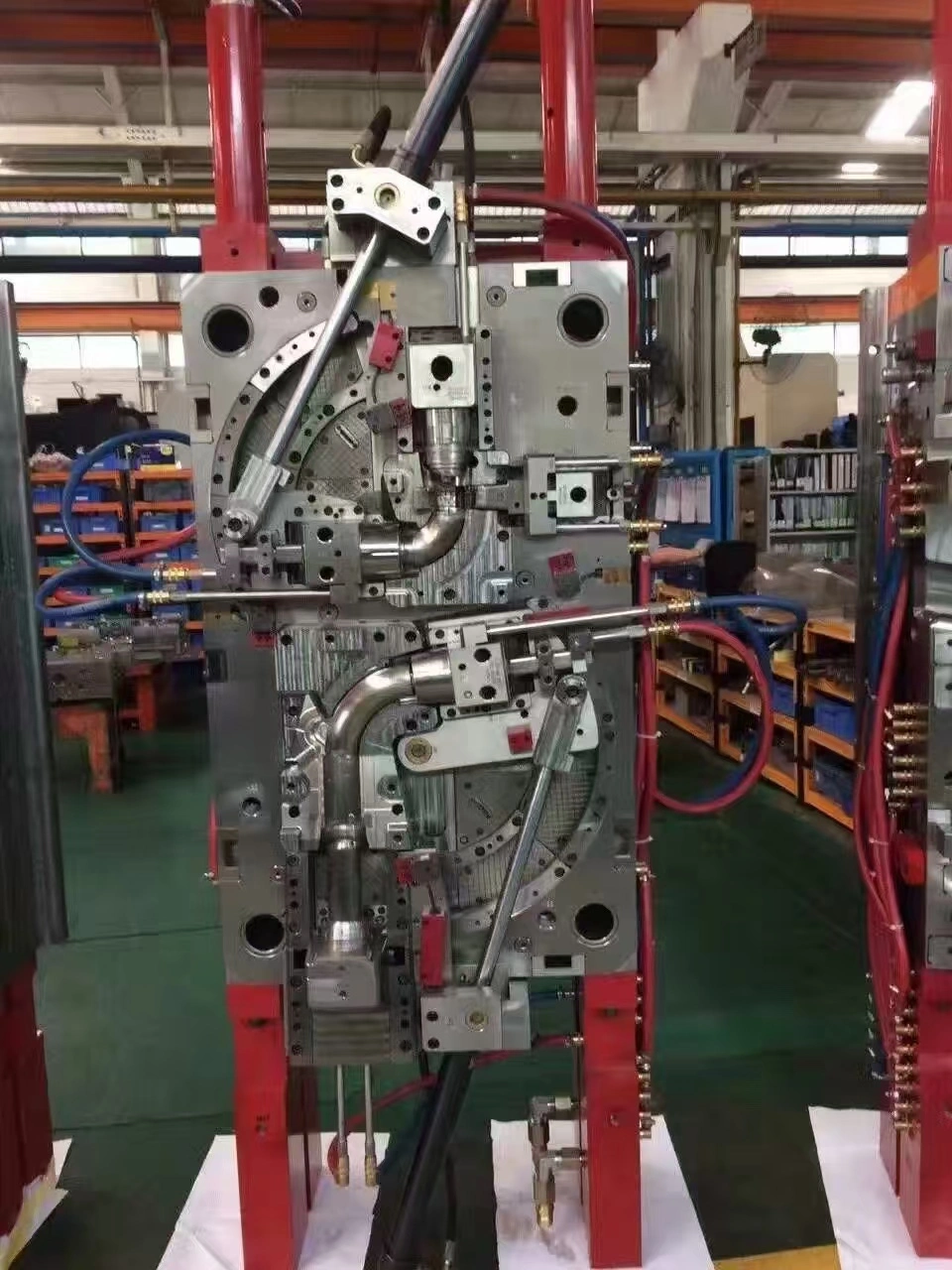
Producing high-quality glass-filled plastic components careful attention to processing parameters and design principles. Our team at Yongsheng has refined these techniques over more than two decades, serving clients who demand precision and consistency in every production run.
Injection Molding Excellence
For medium to large quantities, injection molding is still the most common way to make glass-filled plastic parts because it is repeatable and cost-effective. To do this, the composite material is melted and then injected under high pressure into very precise shapes. Processing temperatures are usually 20–40°C higher than empty resins to make sure the right flow and spread of fibers. During casting, it's very important to keep track of the fiber direction. Glass strands line up with the direction of flow, making anisotropic qualities where strength changes from direction to direction. Expert mold makers take this into account by putting gates and fill patterns in a way that maximizes strength where loads are concentrated. Differences in wall width are very bad for the structure because they cause sink marks, warping, and internal pressures that weaken the structure.
Design for Manufacturability Principles
A well-designed component strikes a balance between the needs for efficiency and the facts of production. Sharp corners cause stress buildup and stop material flow, so designers make sure that all changes have large radii—usually at least 0.5 mm." Draft angles of 1-2 degrees make it easier for parts to come out of the mold and lessen mold wear. Ribbing patterns make things stiffer without using too much material. However, the thickness of a rib should not be more than 60% of the thickness of the wall next to it to avoid sink marks. During the sample process, we always suggest that our engineering team and clients work together on the design. This partnership finds possible problems with manufacturing before investing in tools, which saves time and money. To make sure that designs are best for production, we use design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis to look at part shape, material flow modeling, and the ability to make the right tools.
Environmental and Durability Factors
The long-term success rests on how well the weather protection fits the needs of the product. Glass-filled composites naturally don't react with many chemicals, but the choice of polymer is important for harsh settings. UV stabilizers make things last longer outside, and moisture shields keep things from changing size when it's wet. More and more reclaimed materials are being used in modern recipes to meet environmental requirements without lowering performance. Post-industrial regrind usually mixes in at 15–25% levels, which lowers the cost of materials and supports the ideas of the cycle economy.
Comparative Analysis: Glass-Filled Plastics vs. Alternative Materials
Selecting the optimal material for structural applications requires understanding trade-offs between different options. Glass-reinforced polymers occupy a valuable middle ground, offering advantages that neither standard plastics nor traditional metals fully provide.
Strength-to-Weight Performance
Material replacement is what causes weight loss in many businesses. Glass-filled parts usually weigh 40 to 60 percent less than metal parts of the same size and shape, but they are just as strong in many situations. This weight savings means that cars will use less gas, shipping costs will go down, and it will be easier to put together. A car company recently said that changing twelve steel frames with glass-filled nylon parts saved 3.2 kilograms per vehicle, which is a big deal when you multiply that by the number of vehicles made each year. The strength-to-weight ratio estimate shows that the new parts are much better. Absolute strength is higher in metals like steel and aluminum, but specific strength (strength per unit weight) is very high in glass-filled plastic components. Aluminum has a tensile strength of 310 MPa at 2.70 g/cm³, while 30% glass-filled nylon 6 has a tensile strength of about 150 MPa at 1.35 g/cm³. The specific strength comparison shows that aluminum has a value of 115 MPa/(g/cm³), while glass-filled nylon has a value of 111 MPa/(g/cm³). These are very similar values, and aluminum has extra benefits like being resistant to rust and being easier to build.
Corrosion Resistance and Lifecycle Costs
Unlike metals, glass-reinforced plastics don't corrode on their own, so they don't need safe coatings or upkeep. When exposed to water, salt spray, or chemicals, parts keep their structural integrity and don't break down. This makes it last longer, which lowers the total cost of ownership. Our clients in coastal industrial settings say that switching from coated steel to glass-filled parts stopped recurring corrosion-related failures and the costs of downtime that came with them. A lifecycle cost analysis must take into account the initial cost of materials, the cost of tools, processing costs, and issues related to end-of-life. The cost of materials for glass-filled parts is usually higher per kilogram than for empty plastics but lower than for many metal alloys. When you buy injection molding tools up front, they cost a lot of money. But when you spread out the costs over a lot of pieces, the per-piece costs become very competitive. During processing, less energy is used than during metal casting or cutting, which helps leave a smaller environmental impact.
Thermoplastic vs. Thermoset Composites
Within glass-filled plastics, procurement professionals choose between thermoplastic and thermoset options. Thermoplastic composites dominate high-volume production due to faster cycle times, recyclability, and simpler processing. Materials like glass-filled nylon and PBT can be remelted and reformed, supporting sustainable manufacturing practices. Thermoset composites using epoxy or polyester resins offer superior heat resistance and dimensional stability but require longer cure cycles and generate non-recyclable scrap.
Procurement Insights for Glass-Filled Plastic Components
Strategic sourcing of engineered components involves evaluating multiple factors beyond unit pricing. Successful procurement balances cost objectives with quality assurance, supply chain reliability, and technical support capabilities.
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
When assessing potential manufacturing partners, certification status provides valuable insight into operational maturity. ISO 9001:2015 certification demonstrates commitment to quality management systems, process documentation, and continuous improvement. We earned this certification at Yongsheng because we understand that procurement managers need assurance that every production batch meets specifications consistently.Production capacity and equipment capabilities determine whether suppliers can scale with your business growth. Injection molding press tonnage, auxiliary equipment for material handling, and secondary processing capabilities all impact lead times and cost structures. Our facility operates twenty-four presses ranging from 80 to 1200 tons, enabling us to produce components from small precision parts to large structural elements efficiently. Technical support separates exceptional suppliers from transactional vendors. Access to experienced application engineers accelerates problem-solving during design optimization, material selection, and production ramp-up phases. We maintain an engineering team with expertise in mold flow analysis, mechanical testing, and failure mode analysis to support clients throughout product development cycles.
Minimum Order Quantities and Lead Times
Understanding MOQ requirements helps align sourcing strategies with inventory management objectives. Tooling-specific production runs typically require minimum quantities that justify setup costs and material procurement. Depending on component complexity and annual volumes, MOQs might range from 1,000 to 10,000 pieces. We work with clients to structure initial orders that balance inventory investment with per-piece cost optimization, often recommending phased production releases for new product launches. Lead time expectations should account for multiple phases. New tooling design and fabrication typically requires 8-12 weeks for complex molds, though simpler geometries may complete faster. Production sampling and approval processes add 2-3 weeks before full production release. Once validated, repeat production runs for glass-filled components usually ship within 3-4 weeks, depending on quantities and scheduling. Rush service options exist for urgent requirements, though premium pricing applies.
Pricing Framework and Negotiation Strategies
Component pricing reflects several cost drivers that procurement professionals should understand. Material expenses fluctuate based on resin market conditions and glass fiber pricing, typically representing 30-40% of total cost. Tooling amortization spreads the initial mold investment across projected volumes. Processing costs encompass machine time, labor, energy consumption, and quality control activities. Secondary operations like assembly, testing, or packaging add incremental charges. Volume commitments unlock pricing advantages through economies of scale. Annual purchase agreements that guarantee minimum volumes enable suppliers to optimize production scheduling and negotiate better material pricing from upstream sources. We offer tiered pricing structures that reward long-term partnerships and volume growth, creating mutual value for both parties.
International Sourcing and IP Protection
Global sourcing from manufacturing hubs like China's Guangdong Province provides cost advantages while accessing specialized expertise. The Dongguan region, known as the "Town of Molds," concentrates technical talent and supply chain infrastructure that supports efficient production. Our location in Chang'an Town positions us within this ecosystem, providing access to specialized material suppliers, precision toolmakers, and testing facilities. Intellectual property protection concerns rank highly for international buyers. Reputable manufacturers implement confidentiality agreements, restrict access to proprietary designs, and maintain secure data systems. We treat client specifications and product designs as confidential information, implementing access controls and non-disclosure protocols throughout our organization. Many of our long-term partnerships with electronics and automotive clients demonstrate our commitment to protecting competitive advantages embedded in component designs.
Yongsheng's Expertise in Glass-Filled Component Manufacturing
Since our founding in 1993, we have built Yongsheng into a comprehensive OEM manufacturing partner specializing in precision mold fabrication and component production. Our three-decade journey through China's manufacturing evolution has equipped us with deep expertise in glass-filled plastics and other engineering materials. Located in the heart of Dongguan's mold-making district, our 6,000-square-meter facility houses modern equipment operated by over 300 skilled professionals dedicated to delivering quality and reliability.
Comprehensive Manufacturing Capabilities
Our one-stop service model covers the plastic components product development cycle. During the design phase, our engineering team collaborates with clients to optimize part geometry, select appropriate materials, and validate designs through mold flow analysis. This upfront investment in engineering prevents costly modifications during production and ensures components meet performance specifications. Mold fabrication capabilities represent a core competency that differentiates our service offering. We design and build precision injection molds in-house, maintaining direct control over quality and lead times. Our tooling expertise extends to complex multi-cavity molds, family molds combining multiple part designs, and specialized inserts for overmolding applications. Each mold undergoes rigorous testing and validation before release to production, ensuring dimensional accuracy and cycle time efficiency. Production operations leverage modern injection molding equipment with tonnage capacity matched to component requirements. Process monitoring systems track critical parameters—temperature, pressure, cycle time—to maintain consistency across production runs. Quality control checkpoints throughout manufacturing include dimensional inspection, visual examination, and mechanical testing according to customer specifications. We maintain detailed production records that provide full traceability for every batch shipped.
Industry-Specific Solutions
Our experience spans multiple sectors, each with unique requirements and standards. Electronics manufacturers appreciate our understanding of tight tolerance requirements, ESD-safe handling protocols, and regulatory compliance for materials in electronic assemblies. Automotive clients benefit from our familiarity with PPAP documentation, IMDS material declaration systems, and quality standards like IATF 16949 principles. Consumer goods applications demand aesthetic excellence alongside functional performance. We combine technical molding expertise with surface finishing capabilities to deliver components that meet both engineering and visual requirements. Hardware and industrial machinery applications emphasize durability and dimensional stability across environmental variations—requirements that glass-filled materials address exceptionally well.
Customer-Centric Service Approach
We recognize that successful partnerships extend beyond manufacturing transactions. Our service philosophy emphasizes responsive communication, flexible accommodation of changing requirements, and proactive problem-solving. Project management teams maintain regular contact throughout production cycles, providing status updates and addressing questions promptly. Accessibility matters for international clients. Our proximity to Shenzhen Airport—just 50 minutes away—facilitates convenient factory visits for design reviews, production audits, and relationship building. We welcome procurement teams and product developers to tour our facility, meet our technical staff, and observe production operations. These interactions build confidence and understanding that strengthen long-term partnerships. Many clients who initially approached us for single projects have evolved into strategic relationships spanning multiple product lines and years of collaboration.
Conclusion
Glass-filled plastic components deliver compelling value for structural applications across diverse industries. These engineered materials combine strength, durability, and design flexibility while offering cost advantages and weight reduction compared to traditional metal alternatives. Successful implementation requires understanding material properties, manufacturing processes, and design principles that optimize performance. Strategic procurement considers supplier capabilities, quality systems, technical support, and supply chain reliability alongside pricing factors. As product developers and procurement managers navigate material selection decisions, glass-filled composites deserve serious consideration for applications demanding structural integrity without the penalties of excessive weight or corrosion vulnerability.
FAQ
Which industries benefit most from glass-filled plastic components?
Automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and industrial machinery sectors extensively utilize glass-reinforced parts. Automotive applications include under-hood components, structural brackets, and interior supports where heat resistance and strength matter. Electronics manufacturers specify these materials for connector housings, mounting plates, and enclosures requiring dimensional stability. Consumer goods producers incorporate them in power tools, appliances, and sporting equipment. Industrial applications span pump housings, valve components, and machinery parts exposed to chemicals or mechanical stress.
How do glass-filled plastics impact product durability compared to standard polymers?
Glass reinforcement significantly extends component service life through multiple mechanisms. Increased tensile and flexural strength prevent deformation under load, while enhanced creep resistance maintains dimensions during sustained stress. Wear resistance improves in moving assemblies, reducing friction-related degradation. Heat deflection temperatures rise substantially, enabling use in elevated-temperature environments that would cause standard plastics to soften. Chemical resistance varies by base polymer but generally matches or exceeds unfilled versions. Properly designed glass-filled components routinely achieve service lives of 5-10 years in demanding applications.
What considerations guide transitions from metal to glass-filled plastic components?
Successful material substitution requires careful analysis of load conditions, environmental factors, and assembly methods. Engineering teams should compare mechanical properties under actual use conditions rather than relying solely on material data sheets. Finite element analysis helps validate designs before tooling investment. Manufacturing processes differ significantly—machined or stamped metal parts may require a complete redesign to leverage injection molding advantages. Assembly methods may shift from welding or fasteners to snap fits or ultrasonic welding. Cost analysis should encompass tooling investment, per-piece production costs, and lifecycle considerations. Working with experienced manufacturing partners who understand both materials accelerates successful transitions.
Partner with Yongsheng: Your Trusted Glass-Filled Plastic Components Manufacturer
Yongsheng brings over thirty years of specialized experience in precision mold making and component manufacturing to every client partnership. Our ISO 9001:2015-certified facility combines advanced equipment, skilled craftsmen, and rigorous quality systems to deliver glass-filled plastic components that meet exacting specifications. Whether you need custom design support, rapid prototyping, or scaled production, our comprehensive capabilities support your success. We understand the challenges procurement managers face—balancing cost pressures, quality requirements, timeline constraints, and IP protection concerns. Our team addresses these priorities through transparent communication, flexible service, and technical expertise. Contact our team at sales@alwinasia.com to discuss your specific requirements with our application engineers, request material samples for evaluation, or schedule a factory tour to experience our capabilities directly. As your glass-filled plastic components supplier, we commit to delivering quality, reliability, and responsive partnership.
References
1. Mallick, P.K. (2021). "Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Materials, Manufacturing, and Design, Fourth Edition." CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
2. Society of Plastics Engineers. (2020). "Glass Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastics: Design Guidelines and Material Selection." SPE Composites Division Technical Paper Series.
3. Throne, J.L. (2019). "Thermoplastic Foams and Fiber-Reinforced Polymers." Hanser Publications, Munich, Germany.
4. American Society for Testing and Materials. (2022). "ASTM D638: Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics." ASTM International, West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania.
5. Fischer, J.M. (2018). "Handbook of Molded Part Shrinkage and Warpage, Second Edition." William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, New York.
6. European Commission Joint Research Centre. (2021). "Life Cycle Assessment of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers in Automotive Applications." Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg.

We can provide a one-stop service, including design and development, mold fabrication, production, product processing, etc.

Professional injection mold, die casting mold, plastic products OEM manufacturer