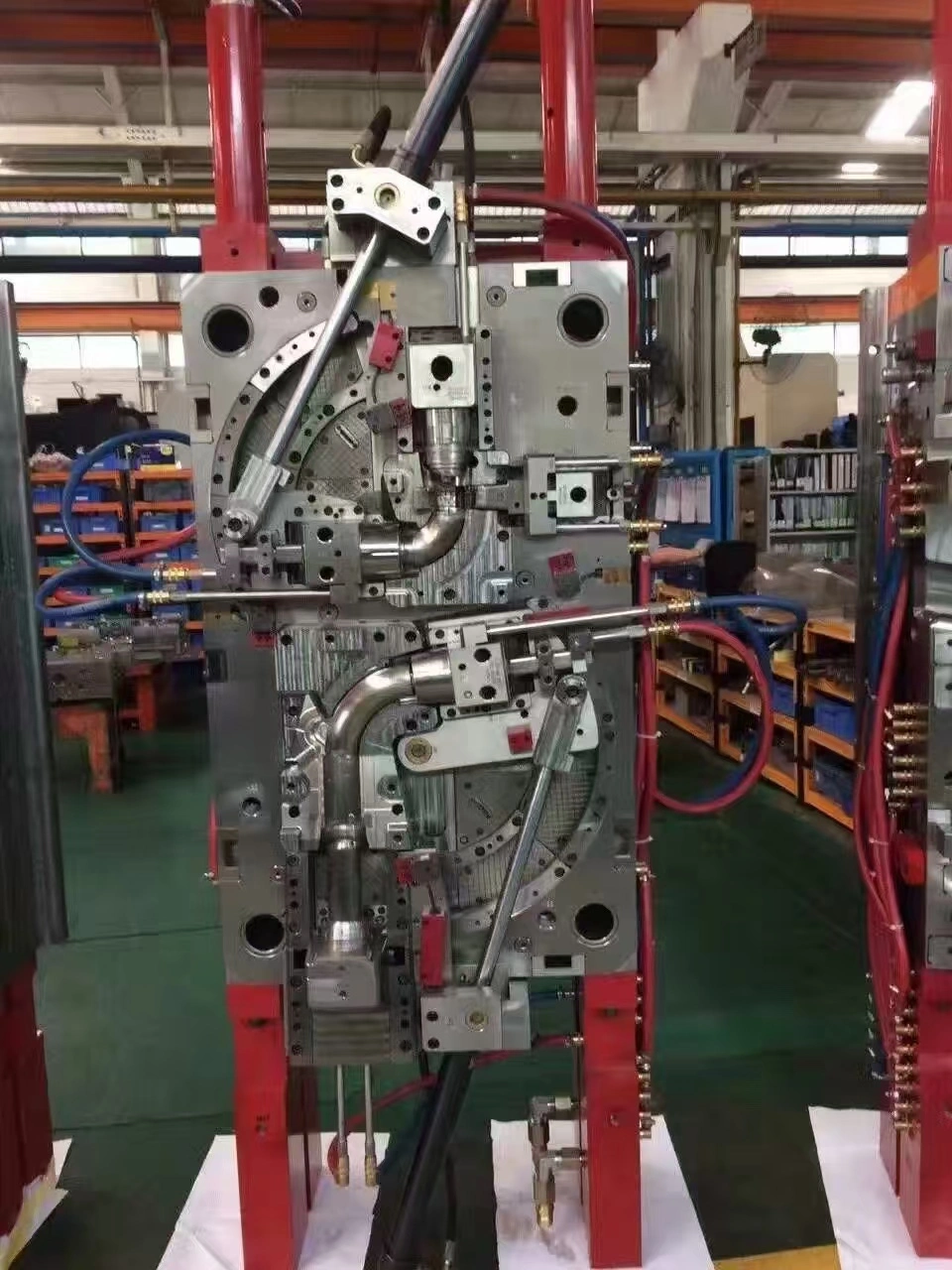
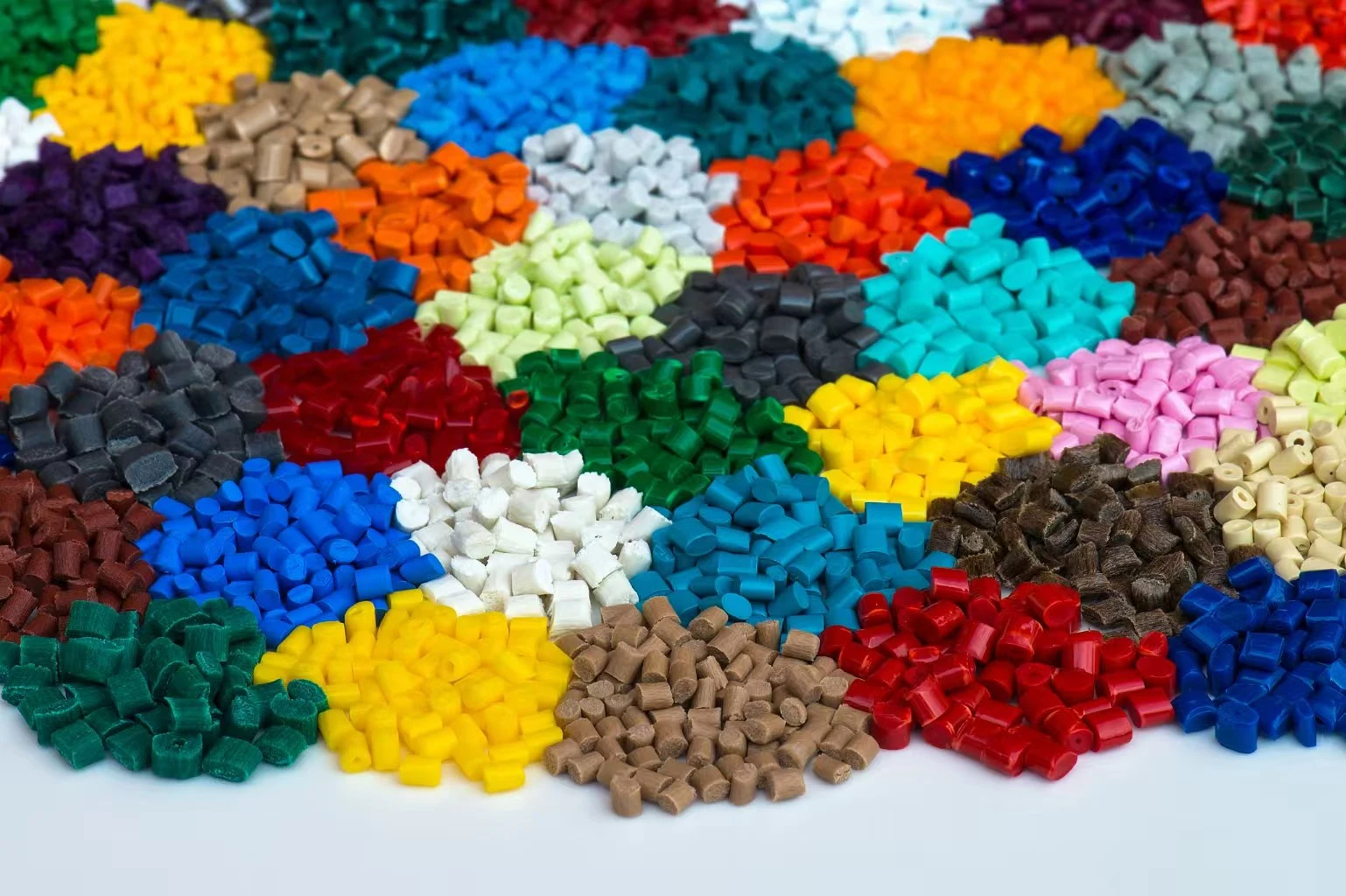
Custom Die Casting for Automotive Components
Custom die casting is one of the most important technologies used in the car industry because it lets engineers make metal parts that are precisely built and meet strict industry standards. In this way of making things, liquid metal is injected under high pressure into steel molds that can be used again and again. This makes parts with very accurate dimensions and a smooth surface. Die-cast parts are used by automakers all over the world for engine blocks, transmission housings, structural frames, and electrical casings. The process is quick, can be repeated, and doesn't cost a lot of money. This makes it essential for both making prototypes and the large quantities that car suppliers need in today's competitive market.

Understanding the Die Casting Process for Automotive Components
Die casting has grown into a complex way to make things that works especially well in automobile settings where accuracy and structural integrity must be maintained. At its core, the process involves pushing liquid metal through hardened steel dies at pressures ranging from 1,500 to 25,000 psi, based on the needs of the part and the way chosen. This high-pressure injection makes sure that the mold is fully filled, even when the shapes are complicated, like when modern car parts have thin walls and lots of small details.
Core Die Casting Methods and Their Applications
Automakers can pick from different types of die casting, and each has its own benefits based on production rate and part specs. When buying, teams know about these methods, and they can make decisions that are in line with project goals and price limits. Most of the cars that are made use a process called high-pressure die casting (HPDC). With this method, liquid metal is injected at very high speeds, filling the die hole in milliseconds. HPDC is great at making thin-walled parts with a smooth surface, which makes them perfect for housing systems and structural braces. The fast solidification reduces the size of the grains, which improves the tensile qualities while keeping the dimensions within ±0.1mm or better. Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) is an alternative method in which controlled pressure, usually between 7 and 100 psi, pushes liquid metal up into the die hole from below. This softer filling method lowers turbulence and gas trapping, making parts with better mechanical features and fewer holes. LPDC is good for things that need to have better structural stability, like suspension parts and wheel systems that need to be resistant to wear. Gravity fixed mold casting and squeeze casting are the last two choices that car engineers have. Gravity casting uses the weight of the metal to fill the body, which saves money when only a small amount is made. During solidification, pressure is applied during squeeze casting to get mechanical qualities that are similar to those of forged parts while still allowing for design freedom of cast parts.
Material Selection for Automotive Die Casting
The choice of material has a big effect on how well parts work, how much they cost to make, and how the car looks altogether. At Yongsheng, we've done a lot of work with the three main types of alloys that are used most often in car die casting. Most car die casting uses aluminum alloys, especially A380, A383, and ADC12. With densities about a third of that of steel, these materials have an amazing strength-to-weight ratio. Aluminum doesn't need extra protective coats because it doesn't rust naturally, and it's great at transferring heat, which makes it perfect for uses like transmission housings and electronic control unit casings. Tensile strengths for parts made from aluminum alloys are usually between 220 and 320 MPa, which is strong enough for most structural uses in cars. Zinc alloys like Zamak 3 and Zamak 5 can be used instead of metal for smaller, more precise parts that need to be very stable in their dimensions. Zinc's lower melting point (around 420°C vs. 660°C for aluminum) makes dies last longer and uses less energy. The material runs very well, which lets you make detailed designs and walls that are thinner than what metal normally lets you do. Zinc alloys are often used by automakers for parts that need to be very precise, like locking mechanisms, sensor housings, and artistic trim. Magnetron metals are the next big thing in efforts to make cars lighter. Because it has a mass of only 1.8 g/cm³, magnesium is 35% lighter than aluminum and 75% lighter than steel. In straight terms, this means better fuel economy and lower pollution. Even though there have been worries about rusting in the past, current magnesium alloys like AZ91D and AM60B have safe alloying elements that make them durable enough for structural parts inside cars, steering wheel cores, and transmission cases.
Advantages of Custom Die Casting in Automotive Components Production
The automotive sector faces constant pressure to reduce costs while improving quality and performance. Custom die casting addresses these competing demands through several inherent advantages that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to match.
Precision and Mechanical Performance
Die casting achieves accuracy in dimensions that eliminates or greatly reduces the need for extra cutting. Tolerances on key measurements are usually kept within ±0.05mm on components, and surface finishes range from 1.5 to 3.0 micrometers Ra right from the mold. The steady, hardened steel tools that don't wear down even after hundreds of thousands of rounds are what make this accuracy possible. High-pressure methods cause materials to solidify quickly, which makes fine-grained microstructures that improve the tensile qualities. Ultimate tensile strengths are often 15-20% higher than sand-cast versions, while stretch values are still high enough for structural use. Die casting's controlled cooling also makes sure that parts have the same mechanical qualities throughout production runs. This reliability is very important in car use, where every part has to meet the same performance standards, no matter when it was made. Instead of dealing with large amounts of differences, quality control teams can set up statistical process controls based on stable, expected results.
Weight Reduction and Fuel Efficiency
Automotive experts are always looking for ways to make cars lighter without lowering their safety or reliability. Die casting makes it possible to make thin-wall shapes that can't be made effectively with other casting methods. In aluminum die molds, wall sections as thin as 0.8 mm are possible, which means that a lot less material can be removed than in machined or forged options. If you die-cast an aluminum gearbox case instead of an iron one, it might weigh 30% less, which directly leads to better gas mileage and lower emissions. This ability to make things lighter goes beyond just using lighter materials. Because die casting gives engineers a lot of design freedom, they can place materials in the best way possible and only add reinforcements where stress analysis shows they are needed. Loads are spread out well thanks to complex rib designs and varying wall widths, which help reach structural goals with little mass.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Die casting equipment takes a big investment up front, but the cost of each part goes down a lot when it's used in large quantities, like in cars. Cycle times for this process are recorded in seconds instead of minutes, and current automatic cells can make hundreds of parts an hour. Over 80% of the materials are used, and all scrap metal can be recycled back into the casting process. When you compare actual cases, the benefits of scalability become clear. From solid stock, a part that needs a lot of cutting might cost $45 per unit at a production rate of 1,000 pieces per year. The same part could cost $12 per unit if 10,000 of them are made each year using die casting, with only a few other steps needed. At 100,000 pieces, the price would drop to $6 per unit. The point where die casting starts to make economic sense is usually between 5,000 and 10,000 units, which is well within the range of most car part uses.
Design Flexibility and Complexity Management
Modern automotive components integrate multiple functions into single assemblies, reducing part counts and assembly operations. Die casting accommodates this trend by producing complex geometries in a single operation that would require multiple manufacturing steps using conventional methods. Integrated mounting bosses, threaded inserts, cooling channels, and cable routing features can all be incorporated directly into the casting design. We've observed successful applications where die casting reduced assembly part counts from fifteen separate components to three integrated castings. This consolidation eliminated fourteen joining operations, reduced inventory complexity, and improved overall assembly reliability by removing potential failure points. The automotive industry particularly values such opportunities where quality improvements accompany cost reductions.
Quality Assurance and Common Challenges in Automotive Die Casting
Maintaining consistent quality in automotive die casting requires systematic attention to process parameters and proactive defect prevention strategies. The automotive supply chain demands zero-defect performance, making quality assurance not merely important but absolutely critical to supplier success.
Common Defects and Prevention Strategies
Porosity represents the most frequently encountered defect in die-cast automotive components. Gas porosity occurs when air or combustion gases become trapped in the solidifying metal, creating voids that compromise mechanical properties and pressure tightness. Prevention requires careful attention to venting design, injection speed optimization, and die temperature management. Modern vacuum-assisted die casting systems evacuate air from the die cavity before metal injection, reducing porosity to levels acceptable even for pressure-critical applications like hydraulic housings. Cold shuts appear as linear discontinuities where two metal streams meet without properly fusing. These defects typically result from insufficient metal temperature, excessive die cooling, or inadequate venting that prevents complete cavity filling. Our engineering team addresses cold shut risks during the mold design phase, optimizing gate locations and flow patterns to ensure metal streams converge with sufficient heat and pressure for complete fusion. Temperature monitoring systems track both metal and die temperatures in real-time, triggering automatic adjustments when parameters drift outside established windows. Shrinkage defects manifest as surface depressions or internal voids in thick sections where inadequate feeding during solidification creates volumetric deficits. Strategic placement of cooling channels, optimized gate sizing, and controlled injection profiles minimize shrinkage. Component designs incorporating uniform wall thicknesses inherently resist shrinkage better than those with abrupt section changes, making early collaboration between casting engineers and product designers essential.
Tolerance Control and Assembly Performance
Automotive assemblies depend on components that fit together precisely without excessive clearance or interference. Die casting processes must consistently deliver dimensions within specified tolerance bands to enable smooth assembly operations. Statistical process control methodologies track critical dimensions across production runs, identifying trends before they result in out-of-specification parts. Control charts reveal when tool wear, thermal expansion, or other factors begin affecting dimensions, triggering preventive maintenance before reject rates increase. At Yongsheng, we implement coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspections on first articles and periodic production samples, verifying up to 100 dimensional characteristics per component. This data feeds back into process optimization algorithms that adjust injection parameters automatically, maintaining stable production even as dies accumulate cycles. Our quality management system, certified to ISO 9001:2015 standards, ensures documented procedures govern every aspect from incoming material inspection through final packaging.
Process Optimization Case Examples
We recently supported an automotive electronics manufacturer struggling with porosity defects in aluminum housings for sensor assemblies. Investigation revealed that excessive injection speeds created turbulence, entraining air into the molten metal. By reducing injection velocity by 20% and extending the intensification phase, we reduced porosity from 12% rejection rates to less than 0.5% while maintaining cycle times. The customer avoided potential field failures and saved approximately $180,000 annually in scrap costs and inspection labor. Another project involved a transmission component experiencing dimensional variation outside tolerance specifications. Thermal analysis revealed uneven die cooling created temperature gradients that affected solidification patterns. We redesigned the cooling circuit to provide uniform temperature distribution, reducing dimensional variation by 60% and bringing Cpk values above 1.67 for all critical features. This improvement eliminated a 100% inspection requirement, reducing quality costs and accelerating throughput.
Choosing the Right Custom Die Casting Supplier for Automotive Components
Selecting a manufacturing partner for automotive die casting projects involves evaluating capabilities across multiple dimensions. The decision extends beyond simple cost comparisons to encompass technical expertise, quality systems, and long-term collaboration potential.
Essential Supplier Evaluation Criteria
Quality certifications provide the foundation for supplier assessment. ISO 9001:2015 certification demonstrates basic quality management system competence, but automotive applications typically require additional automotive-specific standards. Suppliers serving major automotive OEMs should hold IATF 16949 certification, which adds automotive-specific requirements around continuous improvement, defect prevention, and supply chain management. These certifications undergo annual surveillance audits and complete recertification every three years, ensuring ongoing compliance rather than one-time achievement. Tooling capabilities directly impact project feasibility and timeline. Advanced die casting suppliers maintain in-house mold design and fabrication capabilities, enabling rapid iteration during development phases and responsive maintenance during production. Computer-aided engineering (CAE) capabilities allow virtual testing of mold designs before steel cutting begins, identifying potential filling problems, predicting porosity risks, and optimizing cooling channel layouts. These simulation tools compress development timelines and reduce costly physical iterations. Prototyping flexibility separates suppliers capable of supporting product development from those limited to production execution. Automotive product development cycles require multiple design iterations before final production release. Suppliers offering low-volume prototype tooling, rapid sampling capabilities, and responsive engineering support accelerate time-to-market while managing development budgets. The ability to produce 50-100 prototype castings for validation testing before committing to production tooling reduces risk and enables informed decision-making.
Domestic Versus Offshore Manufacturing Considerations
Procurement teams frequently weigh domestic suppliers against offshore alternatives, particularly manufacturers based in China, where labor costs and infrastructure support die casting operations at competitive price points. This decision involves multiple factors beyond simple piece-part pricing. Lead time considerations extend beyond production duration to encompass shipping, customs clearance, and logistics complexity. Domestic suppliers typically offer 8-12 week tooling development timelines and 2-4 week production lead times once tools are validated. Offshore manufacturers might require 12-16 weeks for tooling and 6-8 weeks for production, including ocean freight, though air freight options can compress timelines at increased cost. Organizations operating lean inventory systems with minimal buffer stock may find domestic supply chains more compatible with their operational models. Quality and communication factors influence the working relationship throughout the project lifecycle. Language barriers and time zone differences can complicate technical discussions, though experienced offshore suppliers like Yongsheng employ English-speaking engineers and maintain communication protocols that bridge these gaps effectively. We've invested in technical staff capable of understanding automotive engineering requirements and translating them into manufacturing specifications that meet or exceed customer expectations. Total landed cost provides the most accurate comparison metric. While offshore piece-part pricing may appear 20-40% lower than domestic alternatives, transportation costs, inventory carrying costs, quality inspection requirements, and intellectual property protection measures narrow or eliminate this gap depending on component characteristics and order volumes. Components with high value-to-weight ratios generally favor offshore production, while bulky, low-value items may cost less domestically once all factors are considered.
Yongsheng's Integrated Manufacturing Approach
Since our establishment in 1993, Yongsheng has developed comprehensive capabilities spanning design support through final production, creating a one-stop manufacturing solution for automotive customers worldwide. Our facility in Dongguan's Chang'an Town positions us in China's recognized mold-making hub, where specialized suppliers and skilled craftsmen concentrate. This ecosystem provides access to specialized services and rapid response to unexpected requirements that isolated facilities cannot match. Our 6,000 square meter manufacturing facility houses dedicated areas for mold fabrication, die casting operations, and secondary processing, including CNC machining, surface treatment, and assembly. This integration eliminates coordination challenges inherent in multi-supplier arrangements while maintaining accountability under a single quality management system. When dimensional adjustments require mold modifications, our tooling engineers access the dies directly without shipping delays or communication barriers that external tooling relationships create. We recognize that intellectual property protection concerns many international customers considering Chinese manufacturing partners. Yongsheng maintains strict confidentiality protocols governing all customer information, designs, and technical specifications. Our employee agreements include non-disclosure provisions, and physical and digital security measures prevent unauthorized access to proprietary information. We've maintained customer relationships spanning decades, built on trust and demonstrated reliability in protecting confidential information. Environmental responsibility guides our manufacturing practices as automotive customers increasingly require sustainability throughout their supply chains. Our aluminum recycling systems recirculate scrap metal back into production, achieving material utilization rates above 85%. Modern melting furnaces incorporate heat recovery systems that reduce energy consumption by 30% compared to conventional equipment. These investments align with global automotive industry trends toward reduced environmental impact while controlling operating costs that ultimately benefit customers through competitive pricing.
Procurement Insights: Requesting Quotes and Managing Die Casting Projects
Successful die casting procurement begins with clear communication of project requirements and realistic expectations regarding capabilities and constraints. Preparation and planning during the quotation phase establish foundations for smooth project execution and long-term supplier relationships.
Preparing Effective Quote Requests
Comprehensive quote requests enable suppliers to provide accurate pricing and identify potential technical challenges before commitment. Essential information includes detailed component drawings with dimensional tolerances clearly specified, material requirements including specific alloy designations, surface finish expectations, and annual volume forecasts broken down by release patterns if applicable. Three-dimensional CAD models supplement traditional drawings by enabling virtual mold design and simulation. STEP or IGES file formats maintain broad compatibility across different CAD systems. These digital models allow our engineering team to assess draft angles, identify undercuts requiring side actions, and evaluate wall thickness uniformity without interpretation ambiguity that sometimes affects drawing interpretation. Quality requirements deserve explicit documentation in quote requests. Identifying critical dimensions requiring statistical process control, specifying inspection methodologies and acceptance criteria, and clarifying whether first article inspection reports or production part approval processes (PPAP) apply to the project prevents misunderstandings. Automotive customers should reference applicable industry standards, such as AIAG guidelines, to establish common quality language.
Understanding Cost Determinants
Die casting project costs comprise tooling investment and per-piece production costs. Tooling costs vary dramatically based on component size, complexity, and expected production volume. Simple single-cavity dies for small components might cost $8,000-$15,000, while complex multi-cavity tools for large structural components can exceed $80,000. Slide actions, hydraulic cylinders for complex cores, and specialized surface texturing add to tooling investment but may be necessary to achieve design intent. Production volumes significantly influence tooling decisions and per-piece economics. Higher volume projections justify more expensive, durable tooling incorporating additional cavities and automation features that reduce cycle times. A dual-cavity die costs perhaps 60% more than a single-cavity tool but produces twice as many parts per hour, dramatically reducing per-piece costs at volumes above 50,000 units annually. Our estimating team helps customers optimize tooling specifications based on volume projections and budget constraints. Material costs fluctuate with commodity markets, particularly for aluminum, where global supply and demand dynamics create price volatility. Establishing long-term pricing agreements with periodic adjustment mechanisms protects both parties from extreme market movements while maintaining transparency. We monitor metal markets continuously and communicate proactively when significant cost pressures emerge, working collaboratively to manage impacts through specification reviews or value engineering initiatives.
Managing Timelines and Accelerating Development
Typical die casting project timelines span 16-20 weeks from purchase order to first production shipment. This includes tooling design (2-3 weeks), tool fabrication (8-10 weeks), sampling and refinement (3-4 weeks), and production ramp-up (2-3 weeks). Procurement teams should account for these durations when planning product launches and coordinate tooling release timing accordingly. Accelerated timelines become possible through parallel processing and resource prioritization, though typically at premium costs. Rush tooling programs can compress total timelines by 30-40% through overtime labor, expedited material procurement, and prioritized machine scheduling. We accommodate urgent requirements when customers face unexpected opportunities or competitive pressures, though advanced planning delivers better cost outcomes. Rapid prototyping using 3D-printed sand molds or soft aluminum prototype tools provides functional samples within 4-6 weeks for design validation testing. These approaches produce castings with mechanical properties closely approximating production parts, enabling engineering testing and design verification before production tooling investment. While prototype per-piece costs exceed production pricing significantly, the risk mitigation and development acceleration often justify the investment for complex or unproven designs.
Building Long-Term Strategic Partnerships
Automotive component production extends across vehicle lifecycles spanning 5-7 years, with potential aftermarket demand continuing decades beyond. Suppliers capable of supporting this duration through stable operations, continuous improvement, and capacity scaling create more value than those treating projects transactionally. Yongsheng's experience supporting automotive customers includes relationships exceeding fifteen years where initial component programs expanded into comprehensive manufacturing partnerships spanning multiple product families. These relationships develop through consistent delivery performance, responsive problem-solving, and proactive cost reduction initiatives that demonstrate alignment with customer success. We invest in understanding our customers' roadmaps and technologies, positioning our capabilities to support future requirements as they emerge. Volume scaling capabilities become critical as successful products ramp from initial launch quantities to full production volumes. Our facility employs over 300 skilled team members with the capacity to add equipment and shifts as customer demand grows. We've successfully scaled programs from 50,000 annual units to over 500,000 units within 18 months, demonstrating the flexibility that automotive supply chains require.
Conclusion
Custom die casting delivers compelling advantages for automotive component manufacturing through precision, efficiency, and design flexibility that traditional methods struggle to match. The process accommodates lightweighting initiatives critical to fuel economy improvements while maintaining the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy automotive applications demand. Material options spanning aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys provide solutions for diverse functional requirements from structural housings to precision sensor components. Selecting manufacturing partners with comprehensive capabilities, proven quality systems, and collaborative engineering support ensures project success from initial concept through sustained production. Yongsheng combines over two decades of specialized experience with modern equipment and customer-focused service, delivering reliable manufacturing solutions to automotive customers worldwide.
FAQ
How does die casting differ from sand casting and forging?
Die casting injects molten metal under high pressure into reusable steel molds, achieving tighter tolerances and superior surface finish compared to sand casting, which uses expendable molds. Cycle times are measured in seconds rather than minutes, enabling higher production rates. Forging deforms solid metal through compressive forces, producing excellent mechanical properties but limiting geometric complexity and requiring extensive secondary machining for detailed features that die casting produces directly.
What impact does alloy selection have on component performance?
Alloy selection influences weight, strength, corrosion resistance, thermal properties, and manufacturing costs. Aluminum alloys provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance suitable for structural and thermal management applications. Zinc alloys offer superior dimensional stability and surface finish for precision components. Magnesium delivers maximum weight reduction where corrosion protection measures can be implemented. Our materials engineering team helps customers select optimal alloys based on functional requirements and operating environments.
Which quality certifications matter most when selecting suppliers?
ISO 9001:2015 establishes fundamental quality management system requirements applicable across industries. IATF 16949 adds automotive-specific requirements around defect prevention, continuous improvement, and supply chain management. Automotive customers should prioritize suppliers holding current IATF 16949 certification with clean audit histories. Additional certifications relevant to specific applications include ISO 14001 for environmental management and various customer-specific requirements that major OEMs impose on their supply chains.
Can die casting accommodate low-volume production requirements?
While die casting economics favor higher volumes, prototype tooling approaches enable low-volume production at acceptable costs. Soft tooling using aluminum or pre-hardened steel produces 500-5,000 parts before wear necessitates replacement, providing cost-effective solutions for low-volume applications or product development phases. We work with customers to identify appropriate tooling strategies based on volume projections and budget parameters, sometimes recommending alternative processes when volumes fall below economic thresholds.
How do you protect intellectual property for international customers?
Comprehensive confidentiality agreements govern all customer relationships, with legal protections enforceable under international commercial law. Physical security measures control access to manufacturing areas and engineering offices, while digital security systems protect CAD files and technical documentation. Employee agreements include non-disclosure provisions that survive employment termination. We've maintained decades-long customer relationships built on demonstrated trustworthiness in handling proprietary information, and our reputation depends on continued diligence in this area.
Partner with Yongsheng: Your Trusted Die Casting Manufacturer
Yongsheng brings over 30 years of specialized die casting expertise to automotive component manufacturers seeking a reliable production partner. Our comprehensive capabilities span mold design and fabrication through production and finishing operations, providing true one-stop service that simplifies supplier management. Located in Dongguan's established manufacturing hub with convenient access to Shenzhen logistics infrastructure, we deliver competitive pricing without compromising quality standards. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified operations maintain strict process controls and protect customer intellectual property through documented security protocols. Contact our engineering team at sales@alwinasia.com to discuss your automotive die casting requirements and receive a detailed project quotation from an experienced die casting supplier committed to your success.
References
1. American Foundry Society. (2019). "Die Casting Process and Technology Standards for Automotive Applications." Des Plaines: AFS Technical Publications.
2. Kanicki, D.P. (2020). "Lightweighting Through Advanced Die Casting Alloys in Automotive Manufacturing." Society of Automotive Engineers
3. Die Casting Engineering: A Hydraulic, Thermal, and Mechanical Process. ASM Handbook, Volume 15: Casting. ASM International, 2019.
4. Manufacturing Processes for Engineering Materials. 6th ed., Pearson Education, 2018.
5. Davis, J. R. (Ed.). Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys. ASM Specialty Handbook, ASM International, 2019.
6. North American Die Casting Association (NADCA). Product Specification Standards for Die Castings. NADCA, latest edition.

We can provide a one-stop service, including design and development, mold fabrication, production, product processing, etc.

Professional injection mold, die casting mold, plastic products OEM manufacturer