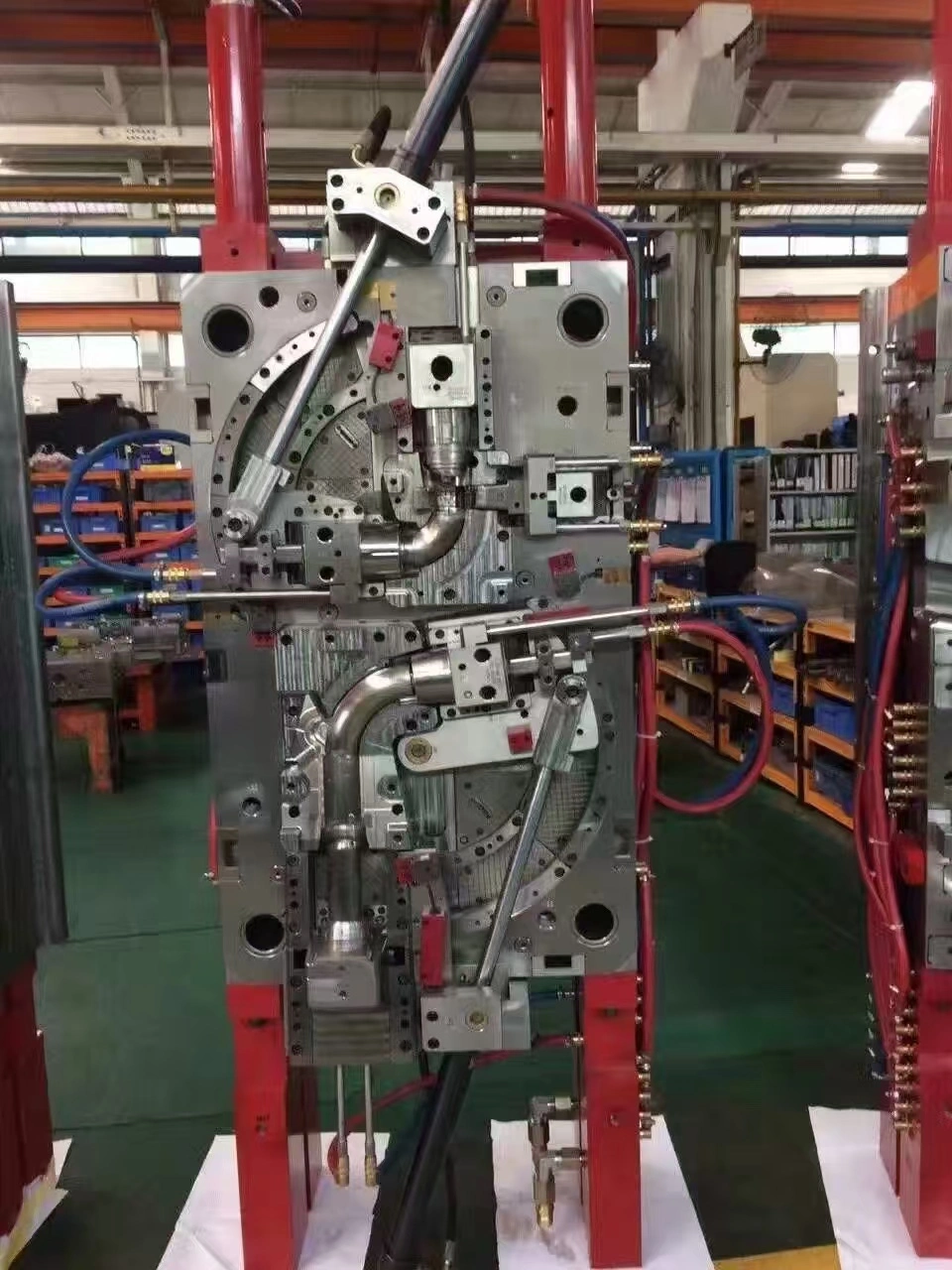
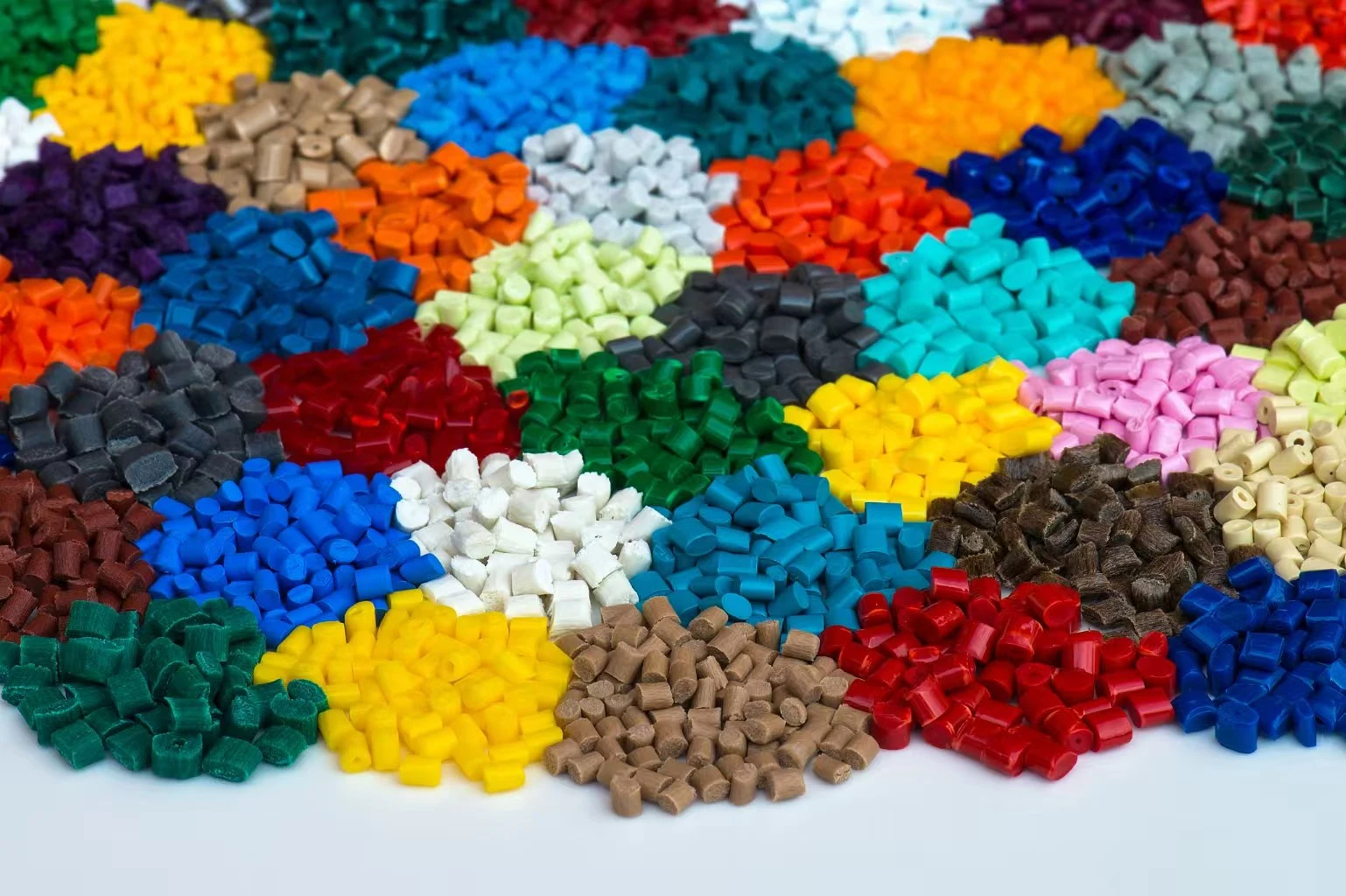
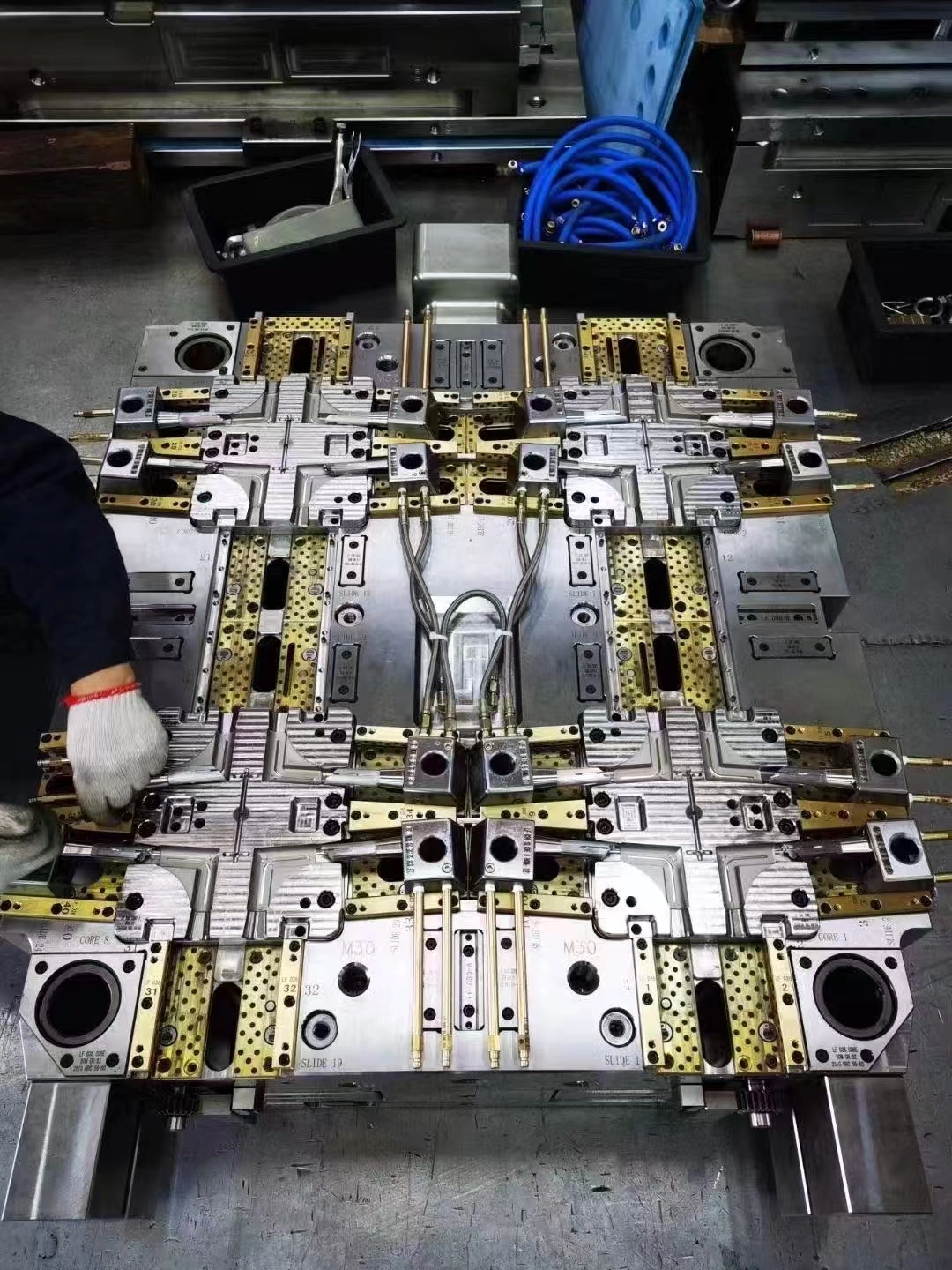
Die casting serves as a cornerstone manufacturing technique in consumer electronics, enabling the production of precise metal components that power our daily devices. This manufacturing process involves injecting molten metal under high pressure into steel molds, creating complex parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Electronics manufacturers rely on die casting to produce lightweight yet durable components that meet the rigorous demands of modern portable devices while maintaining cost-effectiveness at scale.
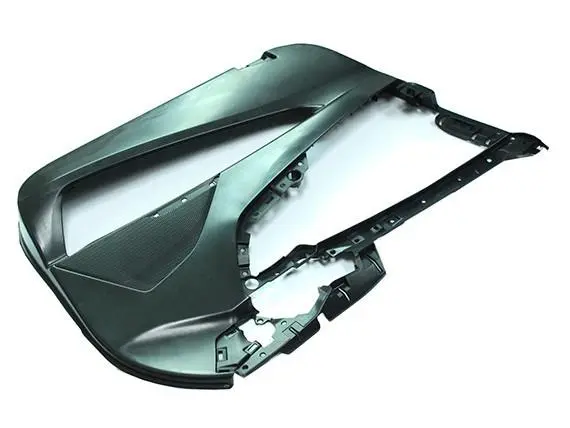

Understanding Die Casting in Consumer Electronics
The die casting process transforms molten metal into precisely formed components through controlled injection into custom-designed molds. This manufacturing technique excels in producing parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances essential for electronic device functionality.
Fundamental Process Mechanics
Die casting works through a orderly approach where liquid metal comes to temperatures between 650°C to 700°C some time recently infusion. The handle utilizes pressure driven or mechanical frameworks to constrain metal into shape cavities at weights extending from 1,500 to 25,000 PSI. This high-pressure environment guarantees total shape filling and disposes of discuss pockets that may compromise component integrity.
The quick cooling cycle permits producers to accomplish generation rates of 100 to 1,000 parts per hour depending on component complexity. This productivity makes pass on casting especially alluring for high-volume hardware generation where reliable quality and dimensional steadiness are paramount.
Material Selection for Electronics Applications
Aluminum combinations overwhelm gadgets pass on casting due to their uncommon strength-to-weight proportion and warm conductivity properties. These materials regularly weigh 65% less than proportionate steel components whereas keeping up basic keenness required for gadget lodgings and warm administration systems.
Magnesium combinations offer indeed more noteworthy weight diminishment, accomplishing densities 35% lower than aluminum. This characteristic demonstrates important for versatile gadgets where each gram impacts client involvement and battery life optimization.
Specific Applications of Die Casting in Consumer Electronics
Die casting technology enables manufacturers to create essential electronic components that balance performance requirements with aesthetic appeal. The process supports diverse applications across multiple device categories.
Protective Housings and Enclosures
Smartphone producers broadly utilize pass on cast aluminum lodgings to accomplish premium aesthetics whereas giving electromagnetic obstructions protecting. These lodgings require divider thickness varieties between 0.8mm to 2.5mm to oblige inside components whereas keeping up basic unbending nature amid every day use.
Laptop chassis speak to another critical application where kick the bucket casting empowers lean profiles without compromising strength. Cutting edge ultrabooks accomplish chassis thickness underneath 15mm through accuracy kick the bucket cast development that coordinating mounting focuses, ventilation channels, and cable directing inside single components.
Thermal Management Solutions
Heat sink fabricating exhibits kick the bucket casting's capacity to make complex blade geometries that maximize surface region for warm dissemination. These components highlight blade dividing as tight as 1.5mm whereas keeping up reliable thickness all through the structure.
Gaming comfort warm sinks illustrate progressed pass on casting capabilities through coordinates vapor chamber mounting focuses and optimized wind stream channels. These plans accomplish warm resistance values underneath 0.5°C/W whereas supporting processor loads surpassing 200 watts.
Structural Components and Brackets
Internal mounting brackets require precise dimensional control to ensure proper component alignment within electronic assemblies. Die casting achieves positional tolerances within ±0.1mm across bracket mounting points, eliminating assembly issues that could affect device functionality.
Overcoming Challenges: Die Casting Defects and Solutions in Electronics Manufacturing
Quality control in electronics die casting demands understanding potential defects and implementing preventive measures throughout the production process. Addressing these challenges ensures components meet stringent electronics industry standards.
Porosity and Surface Quality Control
Gas porosity influences around 15% of kick the bucket cast parts when prepare parameters need optimization. This deformity happens when caught discuss or gas makes voids inside the component structure, possibly compromising mechanical quality and electrical conductivity.
Advanced vacuum pass on casting frameworks diminish porosity occurrences by 80% through controlled air infusion. These frameworks keep up depth weight underneath 100 mbar amid metal infusion, guaranteeing total discuss departure some time recently cementing begins.
Surface wrap up necessities for gadgets components regularly indicate Ra values underneath 1.6 micrometers. Accomplishing these details requires cautious consideration to shape surface arrangement and discharge specialist application protocols.
Dimensional Stability Solutions
Thermal cycling amid gadget operation can uncover dimensional irregularities in kick the bucket cast components. Components encountering temperature varieties between -20°C to +85°C must keep up dimensional solidness inside ±0.05mm to avoid get together failures.
Stress alleviation warm treatment forms dispense with inside stresses that may cause dimensional float over time. These medications include controlled warming cycles at 200°C for aluminum components, taken after by progressive cooling to room temperature.
Comparative Insights: Die Casting vs. Alternative Manufacturing Methods for Electronics
Manufacturing method selection significantly impacts component performance, cost structure, and production timeline. Understanding these relationships enables informed decision-making for electronics procurement teams.
Die Casting vs. CNC Machining
Die casting accomplishes fabric utilization rates surpassing 95% compared to CNC machining's commonplace 30-40% productivity. This contrast interprets to considerable fabric fetched reserve funds for high-volume hardware generation where thousands of indistinguishable components are required.
Production speed favors pass on casting with cycle times between 30 seconds to 3 minutes per portion, whereas CNC machining requires 15 minutes to a few hours for identical complexity. In any case, CNC machining offers predominant dimensional exactness for basic resistance highlights requiring accuracy underneath ±0.02mm.
High-Pressure vs. Low-Pressure Die Casting
High-pressure frameworks exceed expectations in creating thin-walled gadgets lodgings where divider thickness approaches 1mm. The seriously infusion weight guarantees total depth filling indeed in challenging geometries with tall length-to-thickness ratios.
Low-pressure options give prevalent mechanical properties through decreased turbulence amid depth filling. This approach benefits auxiliary gadgets components where extreme ductile quality necessities surpass 300 MPa.
Procurement Strategies for Die Casting in Consumer Electronics
Effective supplier selection directly impacts product quality, delivery reliability, and overall project success. Electronics manufacturers must evaluate multiple criteria to identify optimal manufacturing partnerships.
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
ISO 9001 certification speaks to the least quality standard for gadgets pass on casting providers. Progressed providers keep up extra certifications such as IATF 16949 for car hardware or AS9100 for aviation applications, illustrating capability to meet exacting quality requirements.
Production capacity evaluation ought to assess month to month yield potential, regularly measured in cycles per hour increased by accessible generation hours. Driving providers keep up capacity utilization underneath 85% to oblige critical orders and generation changes common in gadgets manufacturing.
Geographic Sourcing Considerations
Asian providers, especially those based in China's Guangdong Territory, offer taken a toll focal points extending from 25% to 45% compared to Western options whereas keeping up quality guidelines reasonable for hardware applications. Lead times ordinarily extend from 3 to 6 weeks for tooling advancement and 2 to 4 weeks for generation quantities.
Proximity to major hardware fabricating center points decreases coordinations costs and empowers speedier reaction to plan changes. Providers found inside 100 kilometers of major get together offices can give same-day conveyance for critical prerequisites, supporting just-in-time fabricating strategies.
Conclusion
Die casting technology continues to evolve as a critical enabler for consumer electronics innovation, providing manufacturers with the precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness required for competitive market positioning. The process delivers exceptional value through its ability to produce complex metal components with tight tolerances while supporting high-volume production demands. Understanding the various applications, challenge mitigation strategies, and procurement considerations outlined throughout this guide empowers electronics manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding their component sourcing strategies. As device miniaturization trends accelerate and thermal management requirements intensify, die casting will remain an essential manufacturing technique for creating the next generation of consumer electronics.
FAQ
Q: What materials are best suited for die casting in consumer electronics?
A: Aluminum alloys, particularly A380 and A383, provide optimal properties for electronics applications due to their lightweight characteristics, excellent thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Magnesium alloys like AZ91D offer even greater weight reduction for portable devices where minimal mass is critical.
Q: How does die casting improve thermal management in electronic devices?
A: Die casting enables the creation of complex heat sink geometries with integrated fin structures and optimized surface areas that enhance thermal dissipation. The process allows manufacturers to incorporate features like vapor chamber mounting points and directed airflow channels within single components, improving overall thermal performance.
Q: Can die casting accommodate rapid prototyping for new electronics products?
A: Modern die casting facilities offer rapid prototype tooling services using soft tool materials that reduce lead times to 2-3 weeks for initial samples. While these tools have limited life cycles, they enable design validation and functional testing before committing to production tooling investments.
Partner with Yongsheng for Precision Die Casting Solutions
Yongsheng brings over 30 years of specialized experience in precision die casting for consumer electronics applications. Our advanced manufacturing facilities in Dongguan, equipped with state-of-the-art high-pressure die casting machines, consistently deliver components that meet the exacting standards of global electronics manufacturers.
Our comprehensive capabilities span from initial design consultation through full-scale production, offering complete project management for your die casting requirements. We maintain strict intellectual property protection protocols and ISO 9001:2015 certification, ensuring your proprietary designs remain secure throughout the manufacturing process. Whether you need prototype development or mass production volumes, our experienced engineering team provides technical expertise to optimize your components for both performance and manufacturability. Connect with a trusted die casting supplier who understands the electronics industry's unique demands - contact us at sales@alwinasia.com to discuss your next project requirements.
References
1. Smith, Robert J. "Advanced Die Casting Techniques for Electronics Manufacturing." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, Vol. 45, 2019, pp. 234-251.
2. Chen, Wei and Thompson, Michael K. "Material Selection and Process Optimization in Consumer Electronics Die Casting." International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 102, No. 7-8, 2020, pp. 2847-2863.
3. Anderson, Patricia L. "Quality Control and Defect Prevention in High-Pressure Die Casting for Electronic Components." Manufacturing Engineering Review, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2021, pp. 112-128.
4. Kumar, Rajesh and Williams, Sarah. "Thermal Management Solutions Through Precision Die Casting in Modern Electronics." Heat Transfer Engineering Quarterly, Vol. 41, No. 15, 2020, pp. 1289-1305.
5. Brown, David M. "Comparative Analysis of Manufacturing Methods for Electronics Enclosures." Production Engineering International, Vol. 33, 2019, pp. 78-94.
6. Zhang, Li and Martinez, Carlos. "Supply Chain Optimization for Die Casting in Global Electronics Manufacturing." Journal of Operations Management, Vol. 67, No. 2, 2021, pp. 156-174.