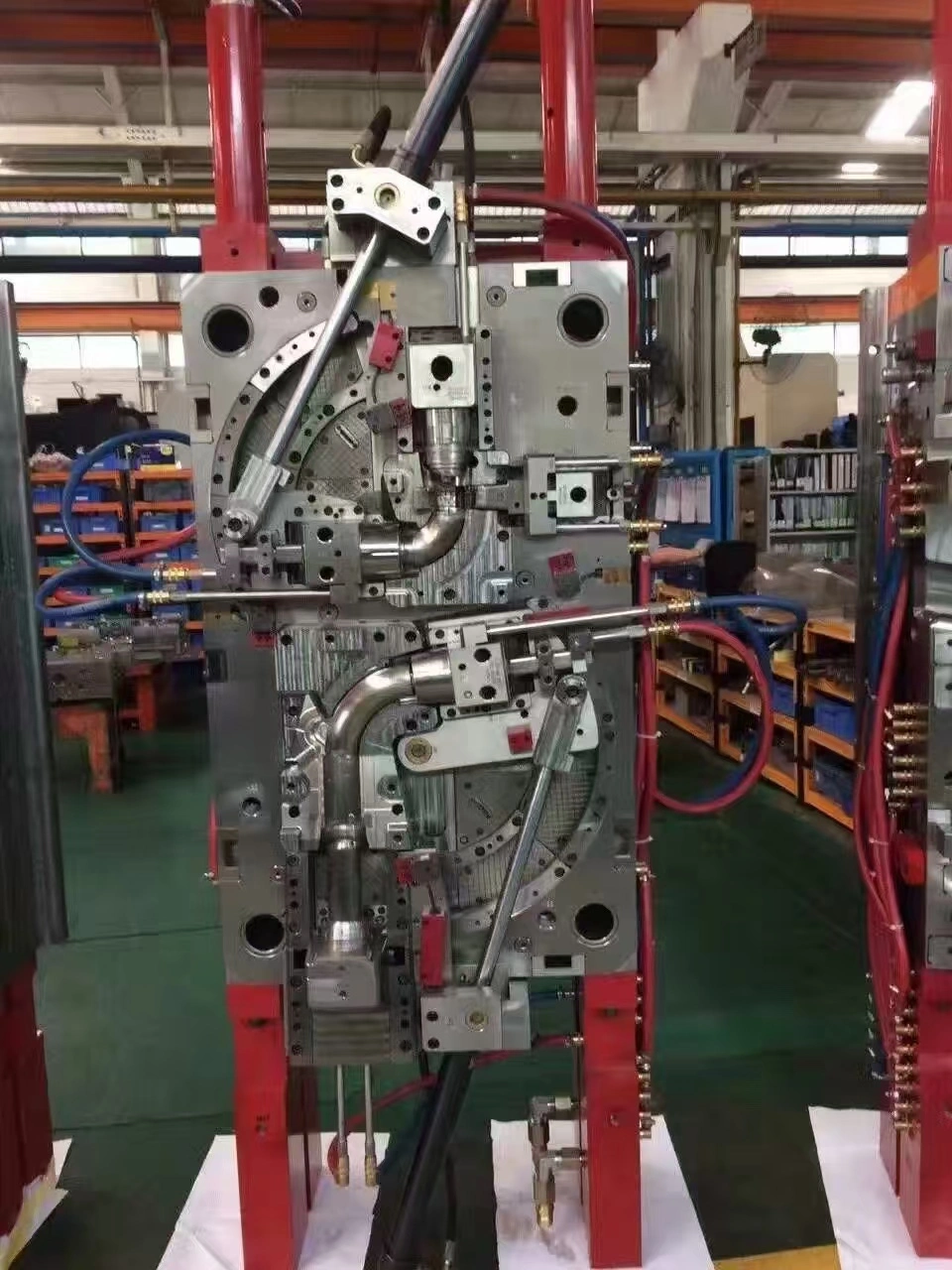
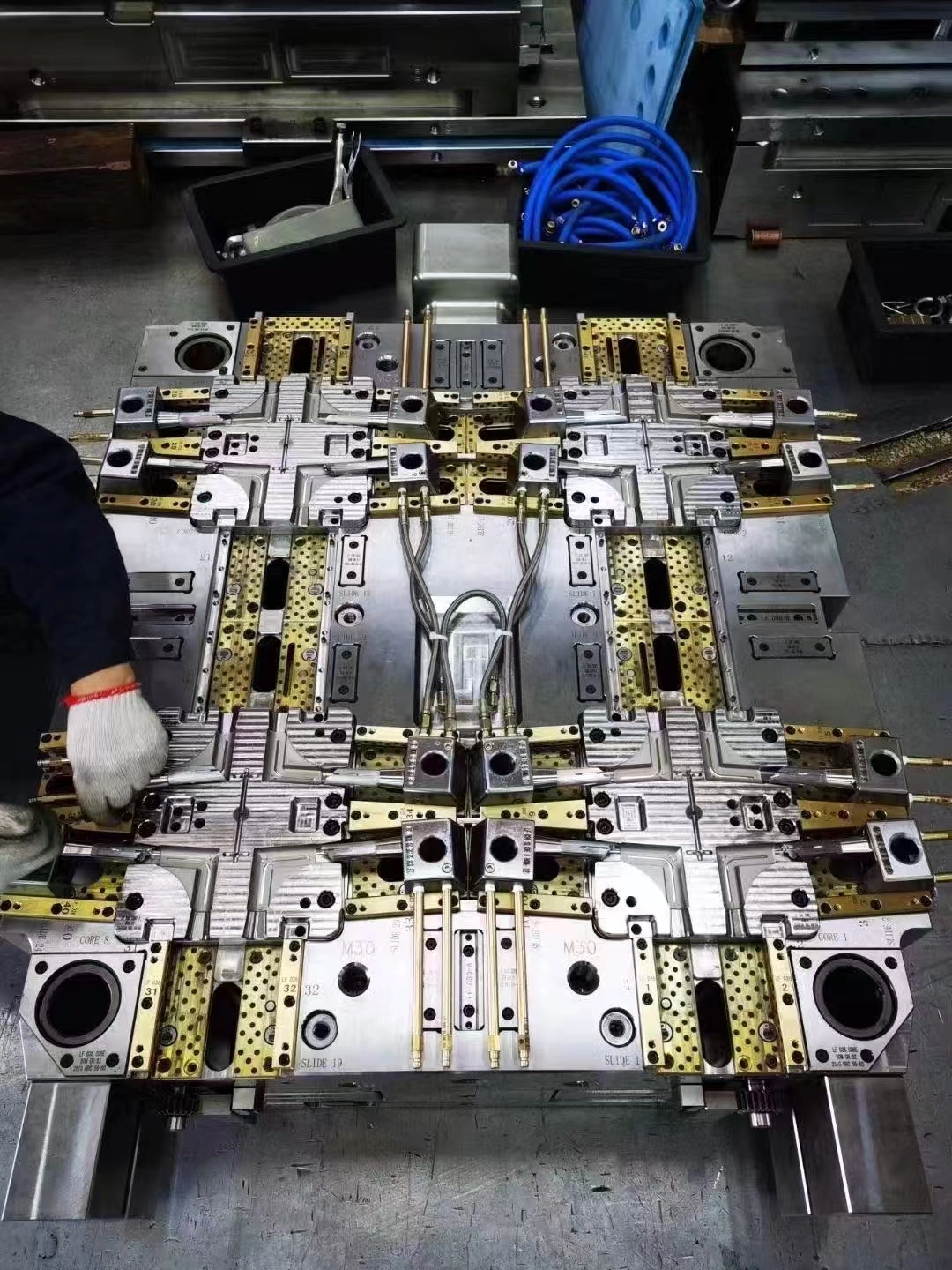
Injection Molds for Medical Device Compliance
Injection molds for medical device compliance are specialized tools made to meet strict standards in the healthcare industry. They allow makers to make safe parts with great accuracy and consistency. These molds have to meet strict rules set by organizations like ISO 13485 and the FDA. They have to be designed in a way that supports clean production areas, material tracking, and accurate measurements every time. Medical-grade injection mold systems are different from regular plastic molding systems because they need validated processes, detailed documentation, and materials that are specifically approved for human contact or implantation. This is to make sure that every part stays safe and effective throughout its clinical lifecycle.
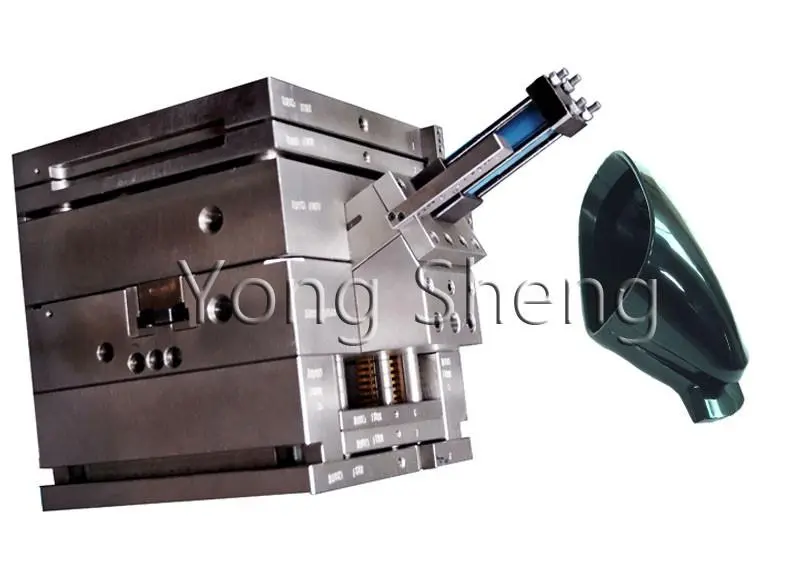

Understanding Injection Molding in Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical gadget business needs ways to make things that are both precise and scalable. Based on our work with healthcare makers, injection molding is clearly the best way to make parts for a wide range of medical devices, from monitoring housings to surgery tool handles. Controlled heating, pressure injection, and quick cooling cycles are used in this process to make medical-grade plastics into exact shapes.
Fundamental Principles of Medical Injection Molding
At its core, the injection molding process depends on four systems that work together. During injection, a lot of pressure is put on the clamping system to keep the two halves of the mold together. When the injection system works, it melts polymer pellets and pushes the liquid material into the mold along runners. Temperature control systems keep the exact temperature conditions needed for certain medical-grade resins. The release device takes finished parts safely, without hurting any delicate parts. When making medical devices, you need to keep a closer eye on every detail than when making consumer goods, because even small changes can affect biocompatibility or device performance.
Custom Mold Types for Medical Applications
Medical device makers can pick from different mold setups based on the number of parts they need to make and how complicated those parts are. For design changes, single-cavity molds are best during the research phase or for specialized low-volume devices because they give you the most freedom. When making a lot of the same parts, like needle tubes or IV ports, multi-cavity manufacturing saves money because the costs of the tools are spread out over thousands of units. We've successfully used family molds to make diagnostic test kits for clients that have a lot of related parts that need to be made in the same cycle. Hot runner systems keep temperatures very low while getting rid of waste from sprues and gates. This is very important when working with expensive biodegradable plastics.
Material Selection for Medical Grade Applications
When making medical equipment, you can choose materials for a lot more than just the finished result. You can even choose materials for the mold itself. To choose the right material, you must first know what the device is supposed to do, how it will be sterilized, and how it will be regulated. Polycarbonate is very clear and can be used for eye inspection tools. Polypropylene, on the other hand, is resistant to chemicals and can be used for cases that hold strong medicines. Liquid silicone rubber is used for implanted devices that need to be biocompatible for a long time. Only sellers who keep full batch tracking and USP Class VI certifications are allowed to give us materials. The mold's base materials must not rust after being sterilized with steam many times, and they must also stay the same size after hundreds of thousands of shots. High-quality tool steels with special surface treatments last a long time, even when working with rough glass-filled materials that are needed for medical parts that support the body.
Ensuring Medical Device Compliance Through Injection Mold Design and Process
Regulatory compliance begins during the injection mold design phase rather than as an afterthought during production. Our design team integrates cleanroom compatibility, validation protocols, and documentation requirements directly into tooling specifications. This proactive approach prevents costly modifications later in the product development timeline.
Design Strategies for Regulatory Adherence
Medical mold design includes features that are specially made to stop pollution and make sure the process works. The placement of gates is carefully thought out to avoid places where germs could get stuck and start to grow. Draft angles are higher than what is normally recommended so that the whole part can be ejected without putting stress on the surface, which could cause tiny cracks that could house germs. Venting systems take air out of holes without making flash, which needs to be trimmed again in a controlled setting. We make sure that all of our wet surfaces have smooth finishes that go above and beyond SPI A-2 requirements. This gets rid of any tiny surface flaws that get in the way of cleaning confirmation. When placing a parting line, engineers think about both how it will affect the speed of production and how it will affect the seal integrity of devices that handle fluids. The shape of each part is improved so that the wall width is the same all the way through. This gets rid of sink marks and other problems inside the part that could weaken its mechanical strength under cleaning stress.
Process Controls and Quality Assurance
Making medical parts requires a level of statistical process control that goes far beyond what is normally expected in industry. Before the first production run, the setup is checked carefully and in writing. This includes dozens of factors, such as the melting point and the time it takes to cool. In-process tracking records injection pressure graphs, finding small changes that could mean flaws before they become parts that don't meet standards. Instead of using sample plans, we use automatic vision inspection systems to check every part for important measurements. When errors happen, our process for investigating them finds the root cause by looking at machine logs, material lot numbers, and the surroundings. Problems like short shots, flash, or sink marks are fixed right away, and paperwork helps with efforts to keep getting better. For traits that are important to quality, this methodical technique has helped our clients get process capability scores above 1.67.
Preventive Maintenance for Sustained Performance
Mold life has a direct effect on maintaining stability in output and compliance. Instead of being based on random time intervals, our preventive maintenance plans change based on real shot counts and process conditions. As part of regular checks, wear patterns on cores and holes are looked at to see if glass-filled materials are wearing away or if certain polymers are attacking chemically. Instead of rebuilding whole mold parts, we repair worn areas using welding and precise cutting. This cuts down on downtime and keeps the original specs. Flow testing is used to check the integrity of the cooling channel because temperature mismatches cause differences in size between cavity places in multi-cavity tools. Instruments for the mold, such as thermocouples and pressure monitors, are calibrated and checked for accuracy at every repair event. This methodical approach safeguards the big investments our clients make in qualified tools while keeping them in the confirmed state needed for legal compliance.
Comparing Injection Molding Solutions for Medical Device Procurement
Procurement professionals evaluating manufacturing technologies for medical devices must balance multiple considerations, including regulatory requirements, production economics, and technical capabilities. Understanding how injection molding compares to alternative processes enables informed decisions aligned with both immediate needs and long-term strategic objectives.
Injection Molding Versus Alternative Technologies
Additive manufacturing technologies like 3D printing offer rapid prototyping advantages and design freedom for complex geometries, impossible with traditional molding. However, material properties differ significantly from injection molded equivalents, and regulatory agencies require extensive validation demonstrating that printed parts match performance claims. Blow molding excels at producing hollow containers but provides less dimensional control than injection processes, limiting its application to less critical components. Compression molding suits thermoset materials and large structural parts, though cycle times extend considerably compared to injection processes. We guide clients through technology selection by mapping device requirements against each method's strengths. Injection molding typically emerges as the optimal choice when projects require high volumes, tight tolerances, regulatory-approved materials, and validated repeatability.
Standard Versus Custom Tooling Economics
The decision between standard and custom tooling hinges on production volume projections and geometric requirements. Standard mold bases accept interchangeable cavity inserts, reducing initial investment for devices still undergoing design refinement. This approach served one diagnostic manufacturer well during their development phase, allowing geometry changes without scrapping entire injection mold assemblies. Custom tooling requires higher upfront expenditure but optimizes cycle time, part quality, and operational efficiency. When annual volumes exceed 100,000 units, the per-part cost reduction from optimized custom molds typically justifies the investment within the product's second year. We provide detailed economic modeling showing crossover points where custom tooling becomes advantageous, helping procurement teams make data-driven decisions that satisfy both engineering and financial stakeholders.
Evaluating Manufacturing Partners
Selecting a molding partner for medical devices requires examining capabilities beyond basic manufacturing competence. Certification to ISO 13485 demonstrates commitment to quality management systems specifically designed for medical applications. We've maintained this certification since 2015, subjecting our processes to annual surveillance audits verifying continuous compliance. Experience with regulatory submissions proves equally important, as manufacturing documentation directly supports 510(k) applications and technical files. Ask potential partners about their cleanroom classifications, as environmental control affects contamination risk for non-sterile devices. Assess their validation capabilities, including installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification protocols. Lead time commitments should account for both tooling fabrication and the validation activities required before commercial production begins. Our typical timeline spans 12-16 weeks from design freeze to validated production, which includes comprehensive first article inspection and process capability studies.
Procurement Strategies for Medical Injection Molds
Sourcing compliant tooling requires strategic planning that extends beyond simply requesting quotes from multiple suppliers. Successful procurement teams develop detailed specifications, establish clear communication protocols, and structure agreements that protect intellectual property while fostering collaborative problem-solving.
Developing Comprehensive Specifications
Effective requests for quotation provide suppliers with complete information needed for accurate pricing and realistic scheduling. Technical drawings should include not just nominal dimensions but also geometric tolerances following ASME Y14.5 standards. Material specifications must reference exact grades and suppliers, as medical-grade resins vary significantly between manufacturers even when carrying similar designations. Identify which dimensions qualify as critical-to-quality characteristics requiring enhanced process controls and 100% inspection. Surface finish requirements deserve explicit callout, particularly for components contacting patients or pharmaceutical preparations. Production volume forecasts should include annual quantities, order patterns, and projected lifespan to help suppliers recommend appropriate tooling durability levels. Regulatory expectations need clear articulation, specifying whether the supplier must participate in design validation, maintain device master records, or support regulatory inspections.
Managing the Product Development Lifecycle
Medical device development typically progresses through distinct phases, each with different manufacturing requirements. Prototype tooling using aluminum or pre-hardened steel accelerates design verification testing, producing parts with properties closely matching production intent. We recommend transitioning to production tooling only after design freeze, avoiding expensive modifications to hardened steel molds. The qualification phase demands rigorous documentation as production processes receive validation. Installation qualification verifies that equipment and tooling meet specifications, operational qualification confirms performance across the operating range, and performance qualification demonstrates consistent production of conforming parts. Throughout commercial manufacturing, change control procedures maintain the validated state when implementing improvements or addressing wear. We partner with clients across this entire lifecycle, adapting our support to match each phase's unique demands while maintaining continuity that preserves institutional knowledge.
Global Versus Regional Sourcing Considerations
Geographic sourcing decisions involve tradeoffs between cost, communication, and supply chain resilience. Asian manufacturers often provide cost advantages stemming from labor rates and material sourcing, though longer lead times and communication complexities require consideration. Our location in Dongguan positions us within China's manufacturing ecosystem while maintaining accessibility to international clients through proximity to Hong Kong and Shenzhen transportation hubs. We've invested in English-fluent project managers and real-time collaboration tools that bridge time zone differences, providing responsiveness comparable to domestic suppliers. Intellectual property protection receives particular attention in our contracts, with clear ownership provisions and confidentiality agreements enforceable through Hong Kong's robust legal framework. Many clients adopt hybrid sourcing strategies, developing tooling with partners like Yongsheng, who offer cost-effective manufacturing while maintaining secondary sources for supply chain redundancy.
Yongsheng's Medical Device Manufacturing Expertise and Solutions
Dongguan Yongsheng Hardware Plastic Product Co., Ltd. brings over three decades of precision manufacturing experience to the medical device sector. Established in 1993, we've evolved from a general plastic molding operation into a specialized partner for companies requiring compliance-focused manufacturing. Our 6,000-square-meter facility houses over 300 skilled employees operating advanced molding equipment, CNC machining centers, and quality verification systems calibrated to medical industry standards.
Our Comprehensive Manufacturing Capabilities
We offer complete turnkey solutions encompassing every stage from injection mold concept through volume production. Our engineering team collaborates during the design phase, applying design-for-manufacturability principles that optimize both part performance and production efficiency. This early involvement has helped clients avoid common pitfalls like undercuts requiring complex tooling or wall thickness variations, causing quality issues. Our toolmaking capabilities span injection molds, die-casting molds, and compression tooling, with specialists experienced in medical device requirements. The production floor accommodates projects ranging from prototype quantities through millions of annual units, with dedicated cells for medical components maintaining enhanced cleanliness protocols. Secondary operations, including ultrasonic welding, pad printing, and assembly, occur in-house, eliminating coordination challenges and protecting intellectual property. This integrated approach provides clients with a single point of accountability, simplifying project management and reducing time-to-market.
Quality Systems and Compliance Infrastructure
Our ISO 9001:2015 certification establishes the foundation for quality management, with procedures and work instructions governing every aspect of operations. We've built upon this framework by implementing medical device-specific controls addressing material traceability, environmental monitoring, and validation documentation. Incoming inspection protocols verify that resins match certificates of analysis and maintain proper storage conditions, preventing moisture absorption or contamination. Statistical process control monitors production parameters in real-time, triggering alerts when trends indicate potential quality drift before defects occur. Our quality laboratory houses coordinate measuring machines, optical comparators, and material testing equipment, providing objective verification of conformance. Every project receives a dedicated quality plan mapping inspection points, acceptance criteria, and documentation requirements to customer specifications and regulatory expectations. This systematic approach has earned us recognition as a trusted supplier to electronics, automotive, and consumer goods manufacturers seeking medical-grade quality standards.
Client Success Stories
One international electronics manufacturer approached us seeking components for a diagnostic medical device requiring FDA clearance. Their previous supplier struggled with dimensional consistency, affecting seal integrity in the fluid handling system. We conducted a thorough design review, recommending gate relocation and cooling optimization that improved wall thickness uniformity. The resulting tooling produced parts with Cpk values exceeding 2.0 for sealing surfaces, supporting successful regulatory clearance and enabling commercial launch within the planned timeline. Another client developing disposable surgical instruments needed a manufacturing partner capable of supporting rapid design iterations during development while scaling to forecasted volumes exceeding one million units annually. Our modular tooling approach accommodated three design revisions without scrapping major mold components, then transitioned seamlessly to production tooling optimized for high-volume efficiency. These partnerships demonstrate our ability to adapt our capabilities to diverse client needs while maintaining the quality and compliance standards medical devices demand.
Conclusion
Injection molding for medical device compliance requires specialized expertise spanning regulatory knowledge, precision manufacturing, and quality system rigor. Successful device development partnerships integrate these capabilities from initial design through commercial production, ensuring components meet both functional requirements and regulatory mandates. Material selection, mold design, process validation, and preventive maintenance each play critical roles in achieving compliant manufacturing. Procurement strategies should emphasize supplier qualifications, comprehensive specifications, and lifecycle management rather than focusing solely on initial tooling costs. By partnering with experienced manufacturers maintaining appropriate certifications and demonstrated medical device expertise, companies can navigate regulatory complexities while achieving cost-effective, scalable production supporting their market objectives.
FAQ
What materials are commonly used for medical-grade injection molds?
Medical injection molds typically utilize high-grade tool steels such as H13, S7, or stainless varieties like 420 and NAK80 that resist corrosion from steam sterilization and cleaning chemicals. These materials maintain dimensional stability across extended production runs while accepting mirror polishes required for cleanability. Cavity surfaces often receive additional treatments like nitriding or PVD coatings, enhancing wear resistance when processing abrasive glass-filled compounds. The mold base components may use pre-hardened steels, balancing machinability with durability for areas not directly contacting molten polymer.
How does injection molding ensure compliance with FDA and ISO standards?
Compliance stems from integrated design and process controls rather than the molding technology itself. Molds incorporate features supporting sterile production, including polished surfaces, optimized venting, and geometry preventing contamination entrapment. Manufacturing processes receive validation through installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification protocols documenting consistent production of conforming parts. Material traceability systems track resin lots through production, enabling investigation if quality issues emerge. Statistical process control monitors critical parameters, maintaining processes within validated ranges. Comprehensive documentation, including design history files, device master records, and batch records, provides evidence supporting regulatory submissions and inspections.
Can small batch production meet medical device regulatory requirements?
Regulatory frameworks accommodate small batch production, provided manufacturers implement appropriate controls. Validation requirements remain identical regardless of batch size, though statistical approaches may adapt to limited sample availability. Process capability studies might extend across multiple batches to accumulate sufficient data demonstrating consistency. Some manufacturers use prototype tooling for limited market release or clinical trials, then transition to production molds for commercial volumes. The key consideration involves maintaining validated processes with documented evidence that manufacturing remains controlled and capable of consistently producing safe, effective devices meeting specifications.
What lead times should procurement teams expect for medical injection molds?
Typical lead times span 12-20 weeks, depending on complexity, though several factors influence duration. Simple single-cavity molds for non-critical components might be completed within 10 weeks, while multi-cavity tools with complex geometries require extended timelines. The design finalization phase consumes 2-3 weeks as engineers optimize tooling for manufacturability and compliance. Steel procurement and machining occupy 6-10 weeks, followed by tryout, sampling, and any necessary refinements. Validation activities, including first article inspection and process capability studies, add another 2-4 weeks before commercial release. Procurement teams should engage potential suppliers early in device development, allowing adequate time for thorough planning rather than compressed schedules that increase risk.
How do manufacturers protect intellectual property when sourcing molds internationally?
Intellectual property protection combines contractual provisions, operational controls, and strategic planning. Comprehensive non-disclosure agreements establish confidentiality obligations before sharing technical information. Manufacturing agreements should explicitly address design ownership, restricting suppliers from producing similar components for other customers. Some companies file patents in manufacturing countries, creating enforceable protections beyond contractual remedies. Operational practices like limiting information sharing to only what's necessary for production reduce exposure. Trusted partners like Yongsheng maintain strict internal controls, preventing unauthorized access to client designs, and have established reputations they protect by honoring confidentiality commitments.
Partner with Yongsheng for Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
Yongsheng stands ready to support your medical device development with comprehensive injection mold manufacturing and production services tailored to regulatory requirements. Our three decades of experience, ISO 9001:2015 certified quality systems, and proven track record serving international manufacturers position us as your reliable partner for custom plastic molds, die-casting molds, and complete OEM solutions. We protect your intellectual property through robust confidentiality protocols while delivering cost-effective manufacturing with on-time performance. Whether you need prototyping support, tooling development, or high-volume production, our team provides the expertise and infrastructure required for medical device success. Contact our experienced injection mold supplier team at sales@alwinasia.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our one-stop service from design through delivery can advance your product goals with confidence and compliance.
References
1. Crawford, R.J. and Throne, J.L. (2002). Rotational Molding Technology. William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, NY.
2. Goodship, V. (2004). Practical Guide to Injection Moulding. Rapra Technology Limited, Shawbury, UK.
3. Kazmer, D.O. (2007). Injection Mold Design Engineering. Hanser Publications, Cincinnati, OH.
4. Mehnen, J., Tiwari, A. and Weinert, K. (2013). Design and Optimization of Medical Device Manufacturing Processes. Medical Device Manufacturing, Volume 7, pp. 234-267.
5. Rosato, D.V. and Rosato, M.G. (2012). Injection Molding Handbook, Third Edition. Springer Science & Business Media, New York.
6. Wen, S. and Zhang, H. (2018). Quality Assurance in Medical Device Manufacturing: Injection Molding Applications. Journal of Medical Device Regulation, Volume 15, Issue 3, pp. 145-178.

We can provide a one-stop service, including design and development, mold fabrication, production, product processing, etc.

Professional injection mold, die casting mold, plastic products OEM manufacturer