Optimize Production with Automated Plastic Molding
Precision, speed, and regularity are all important in modern production, and automatic plastic molding does a great job of meeting those needs. A plastic mold is the most important tool for shaping plastic into exact shapes and sizes. This makes mass production possible in fields like electronics, market goods, home appliances, and cars. Automation turns manual shaping into a more efficient process where robots, sensors, and computerized controls work together to cut down on mistakes, speed up cycle times, and keep quality standards high. With this combination, producers can keep costs down, meet the needs of a growing market, and protect intellectual property all the way through the production process.
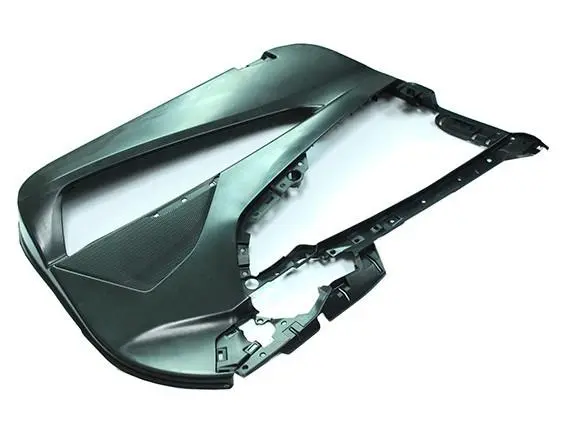

Understanding Automated Plastic Molding
In its most basic form, automatic plastic casting is a technological advance in the way things are made. Precision-engineered tools are used in this process to turn liquid plastic into finished parts by controlling the temperature, pressure, and time. The whole system works with almost no help from a person. It uses high-tech equipment that makes sure it works correctly and consistently over thousands or millions of production runs.
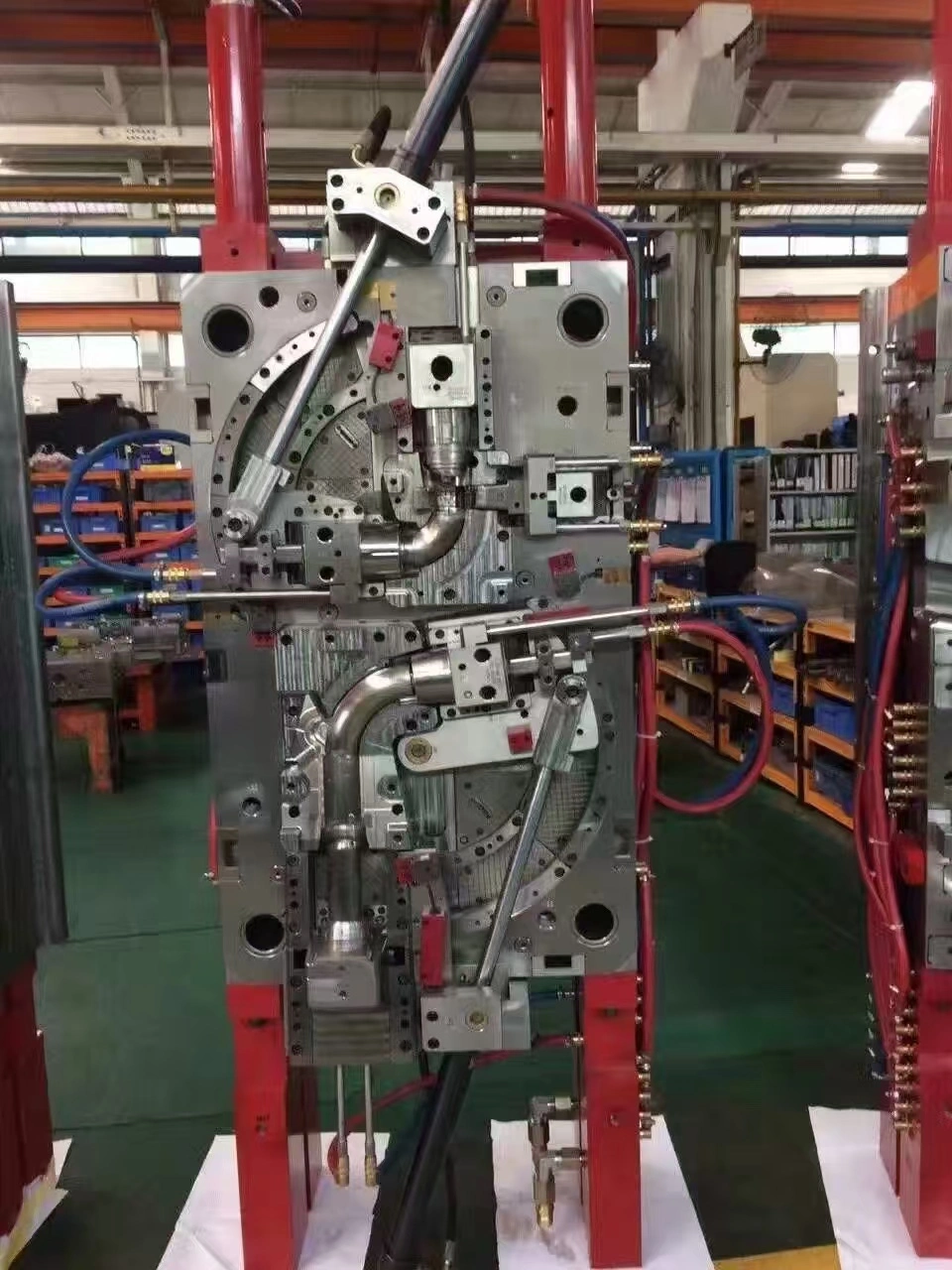
The Critical Role of Molds in Modern Manufacturing
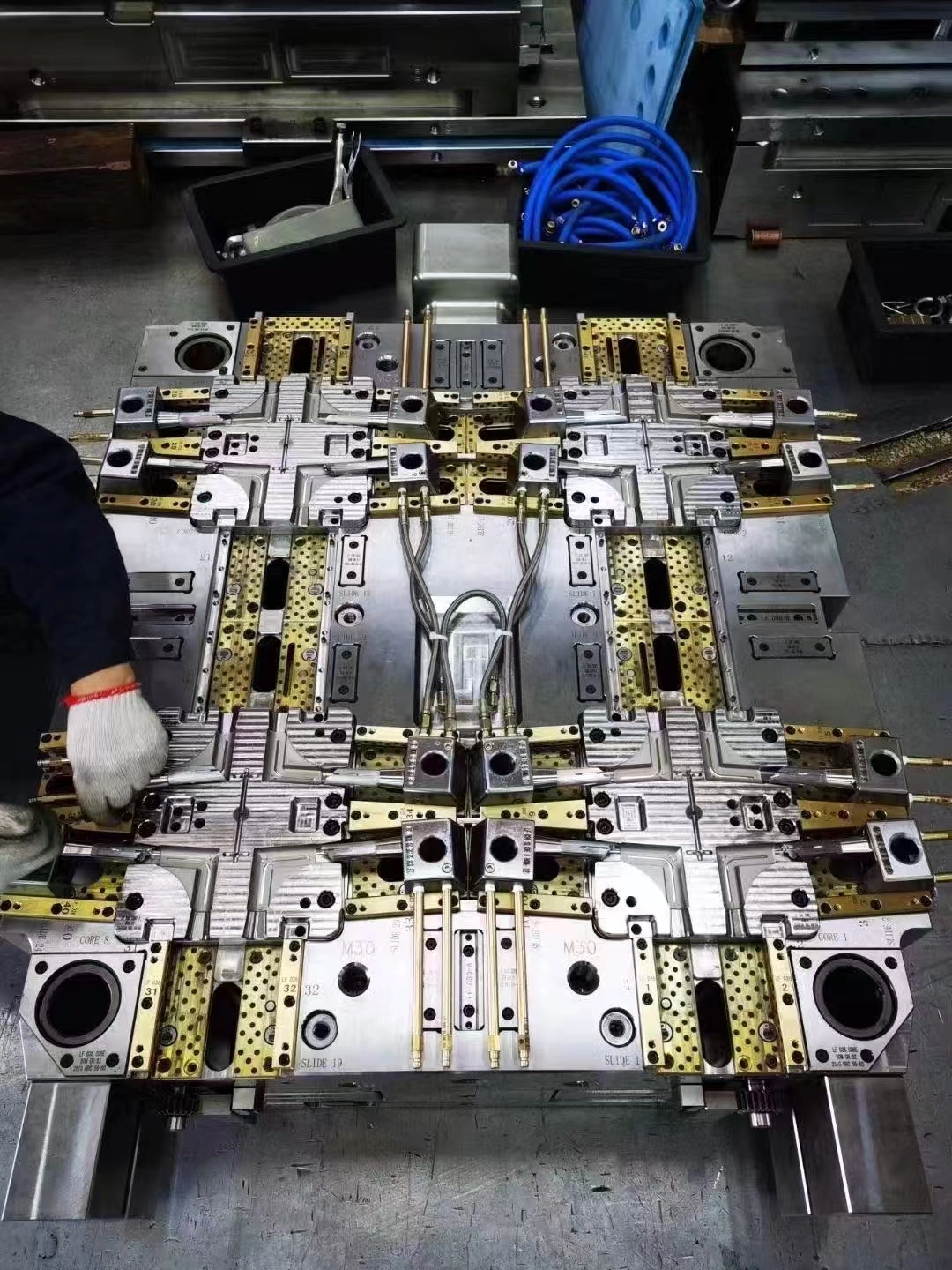
Molds are the most important tools for making plastic parts. These high-tech tools have two main parts: the set mold half and the dynamic mold half. These two parts work together to make the shape that is needed. In addition to these basic parts, modern mold systems have release systems that remove finished parts safely and without damage, pouring channels that move hot material into holes, and temperature regulation mechanisms that control how fast the parts cool. The accuracy of these systems has a direct effect on the quality of the product, its dimensions, and its finish. The steps used in manufacturing depend on the molding technique used, but injection molding is still the most common method used in automatic settings. To do this process, plastic pellets are heated until they melt. Then, the material is injected under high pressure into a closed mold hole. The mold is then kept cool, and the hardened part is ejected. To get the best results, each step needs to be precisely calibrated, which is why automation is so useful for keeping things consistent.
Distinguishing Between Mold Types for Diverse Applications
Professionals in procurement can benefit from knowing the differences between the different types of mold. When complicated shapes and close specs are needed, injection molds are the best way to make a lot of things. Compression molds are better for working with thermosetting plastics or making bigger, simpler forms because they can handle thermoplastics well and support fast spinning. This makes them perfect for housing consumer electronics, interior parts for cars, and gadget parts. Using pre-measured material, an open mold hole is filled, and then heat and pressure are applied at the same time to fix the plastic into its finished shape. This method works well for things like electrical insulators and some parts under the hood of cars, where heat protection is more important than fine detail. Silicone molds are used for specific tasks in development and small-batch production. Their flexibility makes it easier to remove parts and work with undercuts that would make rigid mold designs harder to make. But silicone molds usually can't handle the high temperatures and pressures that come with large-scale automated production, which limits what they can be used for. Besides these main types, manufacturers also use extrusion for pipes and tubing, blow molding for bottles and other hollow containers, vacuum forming for thin-walled packaging trays, and high-foaming polystyrene molding for insulation products. Each method is used for a different set of output needs and materials.
Material Selection: Engineering Factors That Drive Performance
The materials used to make a mold have a big effect on how long it works, how often it needs to be maintained, and how much it costs altogether. Steel molds are the standard for high-volume production because they last a long time and don't wear down easily. Tool steel that has been hardened can be used millions of times without losing its shape, but it is more expensive and takes longer to make, so it needs to be carefully planned out when buying. Aluminum molds are a good alternative when production volumes are medium or when quick tooling turnaround is needed. Aluminum is easier to work with than steel, which cuts down on wait times and the original expense. The material moves heat around well, which speeds up the cooling process and boosts output. But because aluminum is softer than steel, molds may need to be fixed up or replaced more often than steel molds when they are used with rough materials or for longer production runs. Composite materials have become new and useful in some situations, helping to reduce weight and providing unique thermal properties. Some of these modern materials have clay bits or reinforced threads added to them to make them stronger and more resistant to wear, while still having processing benefits over traditional metals. To find the best mix between performance and investment, procurement choices should look at the qualities of the material along with the expected production volume, the complexity of the part, and the budget.
Performance Optimization in Automated Plastic Molding
Traditional manual plastic mold operations face inherent limitations that automation effectively addresses. Understanding these challenges and the technological solutions available helps procurement managers make strategic decisions that enhance manufacturing capabilities.
Identifying Bottlenecks in Conventional Molding Processes
Cycle times and product quality can vary with manual molding systems because they depend a lot on the skill and attention of the person using them. Material placement, mold close pressure, and drying time can be off because of human factors. These differences show up as differences in size, uneven surfaces, and sometimes flaws that aren't found until later stages of quality control. When operators have to manually load materials, watch process parameters, and take out finished parts, throughput is slowed down. The speed and accuracy of automatic systems are too good for even skilled techs to beat. When working with hot materials or under high pressures, or when doing things by hand, the safety risks are also higher. Because of these restrictions, unit costs go up, work times get longer, and the company is less competitive in markets that need quick deliveries.
Automation Principles That Transform Production Efficiency
Modern automatic molding systems get around the problems that came with older systems by using a number of different technologies. Robotic material handling gets rid of the need to load things by hand, which makes sure that everything is put down correctly and frees up workers to do more valuable jobs like quality control and process optimization. These robots work nonstop and don't get tired, so they can keep up the same cycle times over long production runs. Sensors built into the molding equipment give real-time information on important factors like hollow pressure, melt temperature, cooling rates, and cycle progression. Advanced control systems look at this data right away and make small changes to keep things running at their best, even if external factors or material traits change a little. This closed-loop control makes physical consistency much better and cuts down on scrap rates. Using automatic vision inspection systems finds flaws right after a part is ejected. High-resolution cameras take pictures of every part and compare them to digital standards to find flaws on the surface, differences in size, or fills that aren't full. Automatic refuse systems take out parts that don't meet standards before they get to packing. This protects the brand's image and cuts down on waste further down the line.
Real-World Benefits Demonstrated Through Industry Case Studies
One of the biggest suppliers to the car industry added robotic automation to its door handle production line. This cut cycle time by 40% and improved accuracy by 25%. The system works around the clock in three shifts with little control, making 85,000 parts every week compared to 48,000 when it was run by hand. Due to precise shot control and uniform processing conditions, material loss dropped from 6.2% to 1.8%. A company that makes consumer electronics automated their device case molding process by adding robotic insert placement, automated material drying, and in-mold assembly steps. This consolidation cut the damage from handling by 90% and cut the time it took to make the whole thing from 12 days to 4. The investment paid for itself in 18 months thanks to lower labor costs and higher output, which let the company take on more work without having to expand its facilities. These cases show that there are real benefits that go beyond just higher production. Automation helps makers safely grow their businesses, adapt quickly to changes in demand, and keep quality standards that meet strict industry standards. These are all important factors for procurement managers looking for manufacturing partners.
Comparing Molding Solutions for Informed Procurement Decisions
Selecting the appropriate molding approach requires careful evaluation of several factors that impact both immediate costs and long-term performance. A structured comparison helps buyers align manufacturing methods with specific project requirements.
Plastic Versus Metal Molds: Understanding the Trade-offs
Most of the time, people talk about the materials used to make molds, but there are times when metal molding options like die casting need to be thought about. Die-cast metal parts are stronger and can handle higher temperatures better than plastic parts, so they are necessary for structural uses or places where temperatures are high. Metal casting, on the other hand, usually costs more per unit, takes longer, and uses more energy. Plastic parts, on the other hand, work best when weight reduction, electrical protection, or design freedom are important. These days, industrial plastics have great mechanical qualities and are also cheaper and easier to work with. There isn't a clear winner between plastic and metal shaping. Which one to use relies on the function, the cost of production, and the location where the product will be used.
Custom Versus Standard Tooling: Balancing Flexibility and Investment
Standard plastic molds use hole designs that are already known to work with standard forms and sizes. This method cuts down on tooling costs and speeds up project starts, which makes it appealing for situations where design difference doesn't give a big competitive edge. Standard manufacturing works well for basic parts like bolts, housings, or common package elements. Custom molds, on the other hand, give you complete design freedom, letting you make products that stand out by using unique shapes, built-in features, and improved functionality. As part of the development process, designers work together on detailed drawings, prototypes are tested, and exact specs are met through precise cutting. Lead times for unique tools are usually between 8 and 16 weeks, based on how complicated they are. Standard choices, on the other hand, only take 2 to 4 weeks. When a unique product is what makes it successful in the market, or when combining several parts into a single molded part lowers the cost of assembly, the extra investment is worth it. OEM relationships gain a lot when makers can do both special and standard work. This gives procurement teams the freedom to find the best solution for each part on its own, instead of making all of them follow the same buying plan. Standard parts are often used in projects when they make sense, while unique tools are saved for important, customer-facing parts where being different is most important.
Injection Molding Versus Compression Molding: Process Selection Criteria
In automated production settings, injection molding is the most common method because it is fast, accurate, and can work with a wide range of materials. A lot of different thermoplastics can be used in this process. These include common types like polypropylene and ABS, as well as industrial polymers like nylon and polycarbonate. With injection molding, you can make complicated parts with tight standards, fine surface features, and not much post-processing needed. Cycle times are often measured in seconds instead of minutes to meet the high-volume needs of the car, electronics, and consumer goods industries. Compression molding is used for thermosetting plastics that harden during processing instead of melting. To start chemical crosslinking in materials like phenolic resins, melamine, and some silicones, heat and pressure must be applied at the same time. The process works well with fiber-reinforced compounds and bigger parts, which makes it useful for electrical parts, cooking handles, and structural car parts. Cycle times are longer than with injection molding because of the need to cure the parts, but materials are cheaper, and molds don't wear out as quickly because the operating pressures are lower. People in charge of procurement should look at projected production volumes, material needs, dimensional tolerances, and cost goals to figure out which process will best meet project goals. Many makers are skilled in more than one casting technology, which lets them suggest the best method based on the unique properties of each component.
Streamlining Your Procurement Process
Successful sourcing requires systematic evaluation of potential manufacturing partners combined with a clear understanding of cost drivers and quality assurance practices. Strategic procurement approaches reduce risks while optimizing value throughout the supplier relationship.
Global Sourcing Strategies for Identifying Reliable Manufacturing Partners
China has become a top place to get precise molds made and large quantities of plastic parts made. Certain areas, like Chang'an Town, also known as the "Town of Molds," have a lot of specialized knowledge, high-tech tools, and supporting infrastructure. Manufacturers in these places are close to sources of materials, experts in making tools, and transport networks that make operations run smoothly. When looking at Chinese suppliers, purchasing managers should check certifications like ISO 9001:2015, check out facilities through virtual or in-person audits, and ask for detailed customer references from companies in the same industry. North American and European manufacturers are closer to regional markets, communication is easier because of the small time difference, and intellectual property protection systems are already in place. These providers often market themselves as top partners by focusing on tech support, quick prototypes, and team-based development. Costs are usually higher than Asian options, so these sources are best for complicated, low- to medium-volume projects where a technical partnership adds a lot of value. For example, a balanced sourcing strategy might give established Asian manufacturers high-volume, cost-sensitive parts while working with regional suppliers on prototyping, engineering-heavy projects, or production that needs to make many design changes. This method improves both technical response and cost-effectiveness across a wide range of product lines.
Critical Evaluation Criteria That Mitigate Supplier Risk
Along with basic capacity checks, buying teams should look at a number of important indicators that show how reliable a seller is and how likely they are to be a long-term partner. Manufacturing experience in certain industries can be very helpful. For example, a supplier with a lot of experience making automotive parts knows the specific quality standards, documentation requirements, and validation processes that are needed for those applications, as opposed to consumer electronics or industrial hardware. Technical capabilities go beyond basic molding equipment and include in-house design support, mold flow analysis software, coordinate measuring machines for verifying dimensions, and material testing laboratories. Suppliers who offer full services from the initial idea to production ramp-up make it easier to carry out projects and coordinate with multiple suppliers. The way they talk to customers shows how professional they are and how much they care about their customers. Respondent providers keep you up to date on the project on a daily basis, point out any problems that might arise, and show that they can adapt to new needs. Language skills are less important than clear documents, open processes, and a commitment to customer success. When buying abroad, you should pay extra attention to protecting intellectual property. Manufacturers with a good reputation use secrecy agreements, limit who can see secret designs, and keep their data management systems safe. Referrals from businesses in similar industries can give you peace of mind about IP security practices.
Understanding Tooling Costs and Budgeting Considerations
The price of a mold changes a lot depending on the size, complexity, material choice, and level of accuracy needed. Molds with one cavity that make simple forms might cost between $3,000 and $8,000. On the other hand, multi-cavity tools with lots of small features, side actions, and tight tolerances can cost more than $50,000. The number of holes directly affects the cost of making a single unit. Multi-cavity molds cost more to buy at first, but they have much lower piece prices for large orders. The choice of material has a big effect on both the cost of the mold and how long it lasts. Standard tool steel lasts a long time and doesn't cost too much. However, expensive types like H13 or S7 have better wear resistance and are used in production numbers over a million cycles. Aluminum tooling has a lower initial investment than steel alternatives by 30% to 50%. This makes it a good choice for orders below 100,000 pieces or when time-to-market pressures require faster tooling fabrication. Other cost factors include the need for surface finishing, which affects how the part looks and how easily it releases; complexity elements like slides, lifters, and unscrewing mechanisms that allow for complex geometries; and tolerance specifications that require precise machining and a lot of testing. Professionals in charge of buying things should ask for specific quotes that list all of these parts. This way, they can make smart choices about design changes that might save money without sacrificing usefulness.
The Strategic Value of Prototyping and Quality Assurance
Making a prototype checks that plans work before investing in production tools. Modern fast prototype techniques, like 3D printing and CNC cutting, make it easy to make working models quickly. This lets engineers check the fit, the order of assembly, and the performance traits. This validation finds design changes that could cut down on production costs by a large amount or make the product work better. Initial production runs using trial tools or limited-cavity molds give more validation under real processing conditions. These tests show possible problems with shaping, like warpage, sink marks, or fill issues, that computer models might not fully predict. Taking care of these issues during the test phase saves a lot of money on changes to the production tools that need to be made later. Full quality assurance methods build trust in the supplier's abilities. Ask for written information about the checking methods, statistical process control systems, and systems for keeping track of defects. Suppliers should give you reports on measurements, material licenses, and process parameter records that show they have full control over the whole production process. For important uses where a product failing could have major effects, third-party inspection services provide extra checks.
Yongsheng: Your Trusted Partner in Automated Molding Solutions
Establishing successful manufacturing partnerships requires more than technical capabilities—it demands proven experience, comprehensive service offerings, and genuine commitment to customer success. Yongsheng brings over three decades of specialized expertise to every client engagement, combining advanced automation capabilities with customer-focused service approaches.
Three Decades of Manufacturing Excellence
The Dongguan Yongsheng Hardware Plastic Product Co., Ltd. was established in 1993 and has strong roots in Chang'an Town's well-known mold-making area. This stability is due to steady quality service, the ability to react to new technologies, and keeping customers happy even as market conditions change. The fact that the company is a council member of the Dongguan City Hardware Machinery Mould Industry Association shows that it is one of the top manufacturers in the region. The facility is about 6,000 square meters and has more than 300 skilled workers, such as mold designers, process engineers, quality technicians, and production specialists. This level of worker depth lets multiple projects run at the same time without sacrificing personal attention to each customer's needs. Getting ISO 9001:2015 approval is an official way to show that you support quality management systems that keep processes uniform and help them get better all the time.
Comprehensive Capabilities From Concept to Production
Yongsheng is a full-service original equipment maker (OEM) that offers combined services that make buying easier and shorten project timelines. The first level of service is joint design and development support, in which experienced engineers work with customer teams to find the best part shape for performance, cost, and ease of manufacture. When you get involved early on, you can often find ways to combine parts, get rid of unnecessary steps, or choose materials that meet both functional and cost-effective needs. Mold fabrication skills include both plastic injection molds and die-casting molds, which allow for a wide range of material choices across project portfolios. Making tools in-house gives you direct control over accuracy, wait times, and changes, and it keeps your confidential plans safe in secure facilities. The company keeps up-to-date CNC machining centers, electrical discharge machining equipment, and precision grinding tools that make complex plastic mold features to very tight tolerances. Automation technologies are used in production to make things more efficient and consistent. Robots that move materials, check for quality, and keep an eye on the whole process work together to make sure that measurements are correct and that turnover is high. The building can handle projects ranging from prototypes to high-volume production, which supports business growth without customers having to find new suppliers. Secondary processing options, such as assembly, packaging, and surface treatments, make it possible for customers to get the whole product without having to coordinate with multiple vendors. This merging makes handling easier, cuts down on wait times, and gives one person responsibility for the quality of the final product.
Customer-Centric Service Philosophy
High quality, low cost, on-time delivery, and strict intellectual property security are at the top of Yongsheng's list of operating standards. These are the exact things that foreign buying professionals care about the most. The company has strict privacy rules that protect customer designs, specs, and private information at all times during the engagement process. The company's location makes it easier for foreign customers to get their orders. The building is only 20 minutes from the center of Shenzhen and 50 minutes from Hong Kong's airports, making it easy to meet customers, do surveys, and work together. The company encourages on-site checks and runs its business in a way that is open and honest, which builds trust through direct observation. Communication practices stress being clear, quick to respond, and aggressive in fixing problems. Project managers keep everyone up to date on progress, answer questions quickly, and work with people in technical, production, and transportation roles to make sure the project runs smoothly. This attention on the customer goes beyond the original order and includes continued support, technical help, and joint efforts to make things better that make relationships stronger over time.
Conclusion
Automatic plastic mold is a strategic skill that modern makers use to compete in global markets that are very demanding. When you combine precision tools, modern materials, and automation technologies, you get measured benefits like shorter cycle times, better regularity, and lower costs per unit. When purchasing managers know the differences between molding processes, how to choose materials, and how to evaluate suppliers, they can make smart choices that will help both the short-term success of a project and the long-term success of factory relationships. As the needs for production keep changing toward more complexity, tighter standards, and faster delivery times, producers who invest in technology and service models that focus on the customer will become the most popular choice. This way of doing things is shown by Yongsheng, who has 30 years of specialized experience, a wide range of professional skills, and a true dedication to customer success in a wide range of businesses and application needs.
FAQ
What advantages does automated molding provide compared to traditional manual processes?
Automated systems deliver superior consistency by eliminating human variability in material handling, process timing, and quality inspection. Productivity increases dramatically through faster cycle times and continuous operation across multiple shifts. Defect rates decline due to precise parameter control and integrated quality verification. Labor costs decrease while worker safety improves by removing personnel from repetitive, potentially hazardous tasks. These combined benefits reduce overall production costs while improving product quality and delivery reliability.
How should I select appropriate mold materials for my specific application?
Material selection depends primarily on projected production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints. Steel molds suit high-volume production exceeding 500,000 cycles, offering maximum durability and dimensional stability despite higher initial investment. Aluminum provides cost-effective alternatives for medium volumes up to 100,000 pieces or when accelerated tooling delivery is essential. Consider abrasive fillers in your plastic material—glass-reinforced compounds accelerate mold wear, favoring harder steel grades. Discuss specific requirements with experienced manufacturers who can recommend optimal materials based on your complete project parameters.
What lead times and costs should I expect for custom tooling projects?
Custom mold development typically requires 8 to 16 weeks from design approval through first article production, depending on complexity and current shop loading. Simple single-cavity tools for basic geometries start around $5,000, while complex multi-cavity molds with intricate features may exceed $50,000. Costs increase with cavity quantity, precision requirements, mold size, and special features like hot runner systems or automated unscrewing mechanisms. Request detailed quotations that itemize these elements, and consider prototype validation before committing to production tooling to minimize revision risks.
How can I protect my intellectual property when sourcing internationally?
Work with established manufacturers who demonstrate professional IP protection practices through formal confidentiality agreements, secure data management systems, and restricted access to proprietary designs. Request customer references from companies in competitive industries who can validate IP security experiences. Consider registering critical designs in relevant jurisdictions before sharing detailed specifications. Reputable suppliers understand that customer trust depends on absolute confidentiality and implement internal controls accordingly. Yongsheng maintains strict protocols protecting customer information throughout all project phases.
What quality assurance processes should I expect from a reliable molding partner?
Professional manufacturers implement comprehensive quality systems, including incoming material verification, process parameter monitoring, dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring equipment, and statistical process control tracking. Expect documentation including material certifications, first article inspection reports, and process capability studies demonstrating consistent control. Advanced suppliers incorporate automated vision inspection that verifies every component before packaging. Request facility tours or third-party audits to verify actual practices match documented procedures, ensuring production capabilities meet your quality standards.
Partner with Yongsheng for Superior Molding Solutions
Yongsheng stands ready to transform your production challenges into competitive advantages through proven automated molding expertise. As an established plastic mold manufacturer with over 30 years of specialized experience, we deliver comprehensive OEM services spanning design optimization, precision tooling fabrication, high-volume production, and complete secondary processing. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified facility combines advanced automation technologies with rigorous quality management systems, ensuring consistent results that meet the most demanding specifications. We protect your intellectual property through strict confidentiality protocols while providing cost-effective solutions that optimize your manufacturing investment. Our team welcomes the opportunity to discuss your specific requirements, provide detailed quotations, and develop prototypes that validate designs before production commitments. Contact our experienced specialists at sales@alwinasia.com to explore how Yongsheng's integrated capabilities can streamline your procurement process and enhance your product success.
References
1. Rosato, D.V., Rosato, M.G., & Rosato, D.P. (2021). Injection Molding Handbook (4th ed.). Springer International Publishing.
2. Malloy, R.A. (2020). Plastic Part Design for Injection Molding: An Introduction (2nd ed.). Hanser Publications.
3. Kazmer, D.O. (2019). Design and Manufacture of Plastic Components for Multifunctionality: Structural Composites, Injection Molding, and 3D Printing. William Andrew Publishing.
4. Be

We can provide a one-stop service, including design and development, mold fabrication, production, product processing, etc.

Professional injection mold, die casting mold, plastic products OEM manufacturer