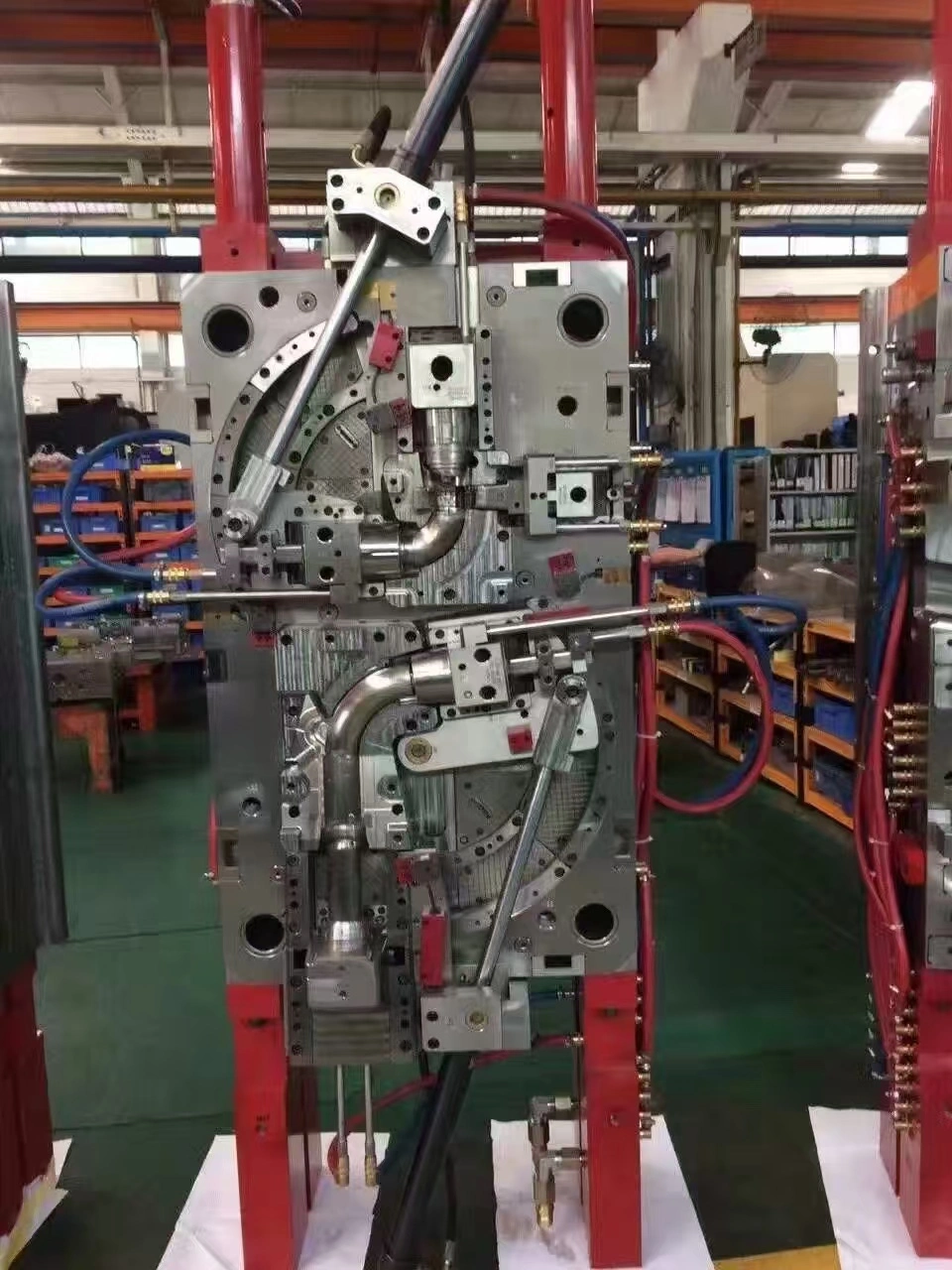
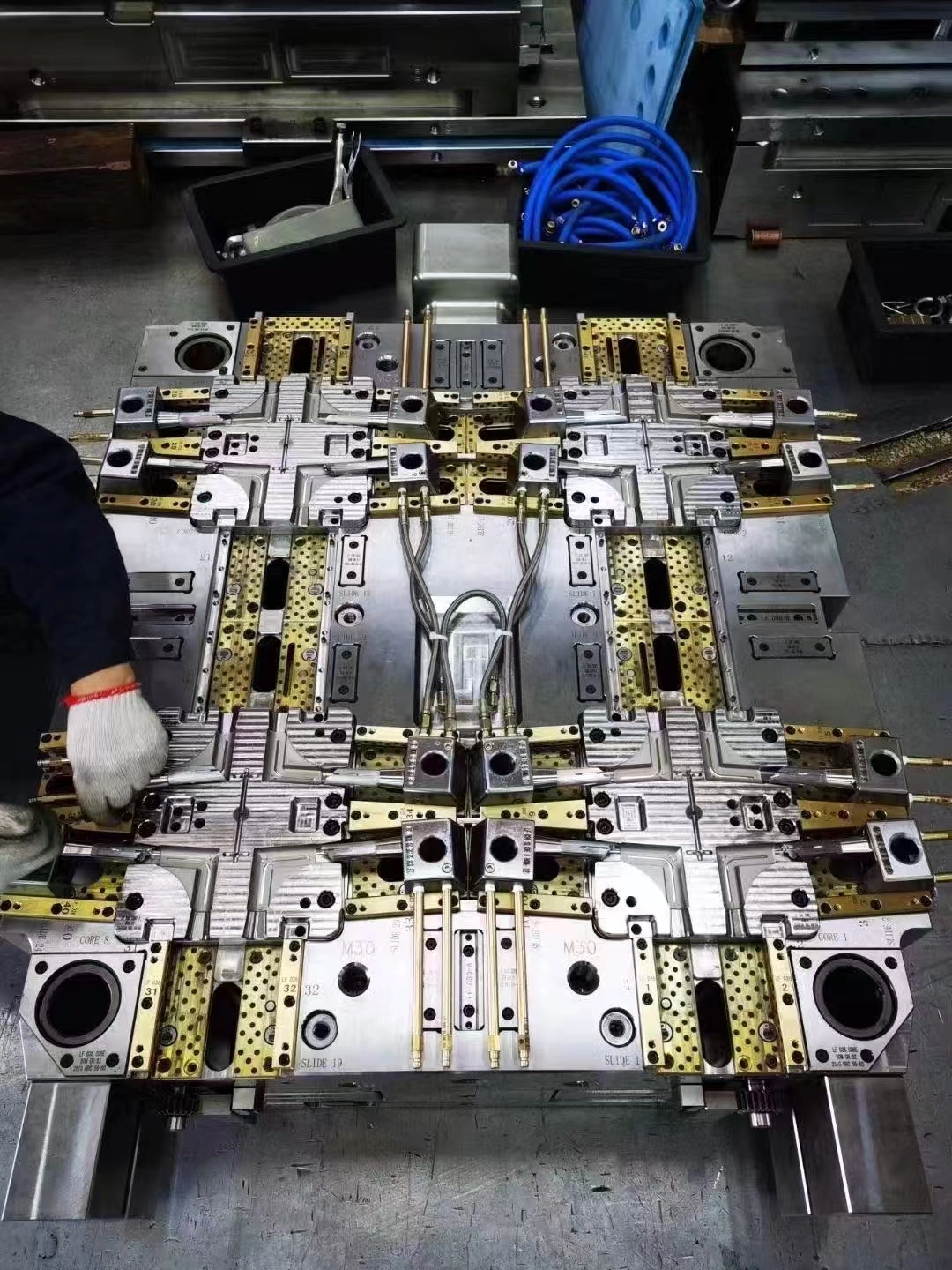
Precision Plastic Components for Automotive Systems
Precision plastic components have changed the way cars are made by providing options that are lighter and less likely to rust, which lowers the weight of vehicles while keeping their structural integrity. These specialized parts include everything from panel sections and interior trim to air intake pipes and fluid tanks that go under the hood. Modern automotive-grade plastics have very accurate measurements, often within 0.05 mm, which means they will work the same way after thousands of production runs. By using more plastic in their vehicles, automakers have been able to reduce the weight of the whole thing, which saves fuel and makes the parts last longer because they are better at resisting chemicals, water, and changes in temperature.

Understanding Precision Plastic Components in Automotive Systems
Defining Precision Plastics and Their Role in Modern Vehicles
Precision plastics are a special type of engineering material that is made to meet exact requirements in harsh vehicle settings. Unlike general-purpose plastics, these materials are carefully made and processed to make sure they always have the same mechanical qualities, don't change in size, and last a long time. These parts are used all over a car, from electrical links that need to fit snugly to structural brackets that hold up important parts. Precision doesn't just mean accurate measurements; it also means being able to predict how something will work in different temperature ranges, when it's exposed to vibrations, and when it comes into contact with chemicals. Modern cars have about 50% more plastic by weight than cars from 20 years ago. This shows that the industry is confident in the abilities of these materials.
Common Types and Their Unique Characteristics
Because they can make complicated shapes with regular accuracy, injection-molded parts are the most common type of plastic used in car parts. High pressure is used to push liquid plastic into precisely made molds. This makes parts with fine details, threaded inserts, and built-in features that would need more than one step to put together using traditional materials. In some situations, composite plastics are just as strong as metals because they are made of resin structures and reinforced threads like glass or carbon. These high-tech materials are used in load-bearing parts, semi-structural parts, and situations where extra stiffness is needed without adding extra weight. Precision automotive plastics are different because they keep their dimensions the same across production runs, don't warp when heated and cooled, and can be used with automated assembly processes. The quality of the surface finish is very important because many parts will be visible in finished cars, or must fit perfectly with closing elements. When choosing a material, it's important to think about a lot of different performance needs at once. For example, a part might need to be able to fight flames, electrical currents, UV light, and impacts all in one design.
Material Selection: ABS, Polyamide, and PEEK
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular material used in car seats because it is strong against contact and has a good finish. It also doesn't cost too much. This material is used in dashboard parts, door panels, and trim pieces where it needs to look good and last a long time. ABS is easy to work with through injection molding, and its surface can be treated in a number of ways, from texture finishing to chrome plating. This makes it flexible for a wide range of design needs. Polyamide materials, which are often called nylon in industrial settings, are stronger and more resistant to heat than ABS. These engineering plastics work great in places under the hood where temperatures can reach 120 to 150°C during normal use. A lot of engine covers, air intake modules, and parts of the fuel system are made of glass-reinforced polyamide, which keeps its shape and doesn't react with oils and fluids in cars. The naturally lubricating nature of the material also helps moving parts like wire guides and latch systems. Polyetheretherketone, or PEEK, is the best car plastic because it performs like metal alloys. This advanced polymer can handle temperatures that are higher than 250°C for long periods of time without losing its mechanical qualities. This makes it ideal for hard uses like transmission parts and high-performance electrical connections. PEEK is much more expensive than regular plastics, but its high toughness and low weight make it worth the extra money in specific situations where failure would have terrible results.
The Manufacturing Process for Precision Plastic Automotive Components
Injection Molding and Advanced Production Methods
Injection molding is still the most common way to make plastic components for cars because it allows for high-volume production and precise control of dimensions. Precision mold design is the first step in the process. This is where skilled toolmakers turn part specs into polished steel holes that can withstand millions of production cycles. Choosing the right material has a big impact on mold design. For example, glass-filled resins need tool steel that is strengthened to resist sharp wear, while normal thermoplastics can use molding materials that are a little softer. Depending on the shape and thickness of the wall, cycle times can be anywhere from 30 seconds for small clips to several minutes for large structural parts. Modern injection molding machines have advanced controls that keep an eye on the pressure inside the cavity, the temperature of the melt, and the rate of cooling in real time. These factors have a direct effect on the quality of the end part, changing things like the surface finish, the amount of internal stress, and the accuracy of the dimensions. Multi-cavity molds make a lot of similar parts at once, which lowers the cost of making each piece by a huge amount for high-volume uses. Family molds work differently; they make several different parts in a single casting cycle, which saves money for low-volume product lines or prototype development. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, plays an important role in developing car parts. We use this technology a lot to test prototypes so that design teams can see how they look, how they fit, and how they work before investing in expensive production tools. Recent improvements in industrial 3D printing make it possible to directly print parts for low-volume cars or repair parts. However, for mass production, speed and material properties currently keep this method from replacing injection molding. The technology is very good at making complicated internal shapes that can't be made with traditional modeling. This opens up new design options for things like custom air ducts or better mounting mounts.
Design for Manufacturability Principles
To create successful car parts, you need to know a lot about the limitations and possibilities of making. Uniform wall thickness stops internal pressures and sink marks, and a standard thickness of 2 to 4 mm is usually the goal, but this depends on the size of the part and its structural needs. Draft angles help the mold come loose, and surfaces that are not parallel to the mold opening direction usually need to be tapered by 1 to 3 degrees. Sudden changes in thickness make it harder to mold and put stress on the material during use, so gradual changes through radiused blends are important for design. Rib structures are stiff without using too much material, but they need to be carefully planned to avoid molding flaws. As a general rule, the width of the ribs shouldn't be more than 60% of the standard wall thickness. There should also be enough space between straight ribs to keep material from building up. Corner curves do more than one thing: they spread out stress in heavy parts, make it easier for material to move during casting, and extend the life of the mold by getting rid of sharp edges that wear down quickly. When physical conditions allow it, experienced designers use large radii, usually starting with numbers equal to the width of the wall.
Quality Control Standards and Testing Protocols
Suppliers to the automotive industry have strict quality control systems in place. ISO/TS 16949 is the standard that governs production methods in this industry. This framework requires written instructions for every step of the manufacturing process, from checking the materials that come in to making sure the finished product works. Statistical process control constantly checks key factors to spot trends before they lead to parts that don't meet standards. For each important feature, control plans spell out how often to measure, what the accepted ranges are, and how to fix problems. Coordinate measuring machines are used for dimension verification to probe part surfaces with micron-level accuracy and compare the real shape to CAD models. In functional testing, parts are put through temperature cycles, sound exposure, and mechanical loads that are similar to how a car works. Standardized studies that measure tensile strength, impact resistance, and external stress cracking resistance are used to confirm the characteristics of materials. Appearance standards say what kind of surface quality is accepted. They cover things like color consistency, gloss level, and the number of visual flaws that are allowed. These thorough quality controls make sure that parts work as they should for as long as they're supposed to, which for cars is usually 10 to 15 years.
Comparing Plastic Components with Alternatives in Automotive Systems
Strength, Weight, and Performance Analysis
When it comes to cars, where reducing mass directly improves fuel economy and vehicle handling, the strength-to-weight advantage of designed plastic components becomes even more appealing. A plastic part usually weighs 40–50% less than a metal part that does the same job. This saves a lot of money when you add up the hundreds of parts that go into a car. The lower weight makes a real difference in meeting corporate average fuel economy goals. It is thought that every 10% reduction in vehicle weight makes it 6–8% more fuel efficient. In many situations, metals are stronger than plastics, but when looking at an application-specific analysis, plastics often meet requirements and offer extra benefits. During normal use, a door handle assembly might be put under 500 Newtons of force, which is well within the strength of glass-reinforced polyamide. This material also has hinges built in and won't rust as die-cast zinc does. Plastic intake pipes are lighter and have complicated internal paths that improve airflow. This shows that choosing the right material can lead to practical changes that go beyond simple replacement.
Composite Materials and Cost Considerations
Carbon fiber reinforced plastics are the best composite materials in terms of performance. They are stiff and strong, almost like aircraft aluminum metals, but they are much lighter. These materials are used in high-performance cars where saving weight is more important than saving money. They are used in basic frame parts, body panels, and suspension parts. At the moment, manufacturing complexity and material costs keep many people from using them, but as production volumes rise, the economics slowly get better. Glass fiber reinforced composites offer a practical middle ground, offering big performance gains over unfilled plastics at reasonable cost increases. We often use glass support in structural braces, mounting points, and load-bearing housings where using only plastics would require walls that are too thick. The percentage of reinforcement ranges from 15% for a small increase in strength to 50% for the best mechanical features. The percentage of reinforcement has an impact on the cost of the material, the trouble of processing it, and the quality of the surface finish. When you do a total cost analysis, you have to take into account extra benefits like resistance to rust and the ability to combine parts into one that requires less setup work and no screws.
Total Cost of Ownership Perspective
Buying choices that are only based on piece price often miss important cost factors over the life of the product that favor plastic parts. Corrosion protection gets rid of the need for regular upkeep, like preventing rust and replacing parts that break down in harsh environments. Integrated snap features, live hinges, and molded-in color that eliminates the need to paint all make assembly faster and easier. Having lighter parts lowers the cost of shipping, makes installation easier, and saves fuel over the life of the vehicle. When making simple shapes, the cost of tools for injection molding is usually higher than for metal stamping or die-casting, but when making complex shapes, the relationship changes dramatically. For example, a plastic part with many features, threaded inserts, and small details might only need one mold. On the other hand, a metal part with the same features would need progressive stamping dies, secondary machining, and assembly fixings. The number of parts made has a big impact on economic analysis. Low volumes support methods that require little investment in tools, while high volumes spread the cost of expensive, precise molds over millions of parts. Procurement workers with a lot of experience look at all of these factors together, knowing that the lowest price per item doesn't always mean the lowest total cost.
Procurement Strategies for Plastic Components in Automotive Manufacturing
Supplier Evaluation and Selection Criteria
Beyond price, there are other factors that need to be looked at when looking for skilled production partners. Quality licenses give you a basic level of peace of mind. For example, ISO 9001 shows that a company is good at making things in general, and IATF 16949 shows that it is good at making cars. As approval status changes over time, we suggest checking certifications on registration websites instead of just taking the paperwork that is given. Production capacity review looks at both how well the equipment works and how much it can produce. A provider may have fifty injection molding machines, but not the exact amount that your part needs. They may also have the right equipment, but not enough ability to meet your volume needs while also meeting their other obligations. Transparency in lead times is very important. Reliable suppliers give realistic timelines that account for mold making, sampling iterations, and production ramp-up, instead of overly optimistic estimates that cause problems later on in the schedule. Technical capability evaluation goes beyond equipment lists to look at engineering support, material expertise, and problem-solving experience. Suppliers who add value by suggesting better designs, different materials, and proactive quality improvements show that they want to work with you as a partner instead of just as a supplier. When it comes to geography, shipping prices and wait times are weighed against how well people can communicate and protect intellectual property. For high-volume parts, being close to the final assembly plant makes handling easier.
Best Practices for Custom Component Procurement
A thorough description of requirements that makes clear functional needs, performance standards, and quality goals is the first step to successful custom component buying. Misunderstandings can be avoided by using detailed sketches that show exact measurements and tolerances, and functional requirements papers that explain how parts work together in bigger systems. When possible, material requirements should be based on industry standards. This gives suppliers clear goals for mechanical properties, resistance to external factors, and processing properties. Before committing to large production numbers, suppliers should be tested through prototype and trial stages to make sure they can meet the goals. We suggest asking for at least three sample rounds. The first round should show basic measurement capability, the second round should include feedback and improvements, and the third round should be pre-production samples from production tools to check the final quality. This step-by-step method finds possible problems early, when fixing them is still affordable, instead of finding them after the expensive production molds are finished. It helps when negotiating prices to know what causes costs to rise and fall in injection molding operations. Material costs usually make up 40 to 60 percent of the price of a standard plastic component. Other costs include manufacturing fees, machine time, and quality verification. By planning production more efficiently and buying materials in bulk, volume agreements make it possible to get better prices. Payment terms have a big impact on a supplier's cash flow. For example, deposit arrangements for investing in tools are set against milestone payments linked to sample approval and production delivery.
Yongsheng: Your Trusted Manufacturing Partner
Yongsheng has been in business since 1993 and has over 30 years of experience in its field. It has become a complete OEM maker for foreign companies in the automobile, electronics, and consumer goods industries. Our building is in Chang'an Town, Dongguan, and it's 6,000 square meters. It has 300 skilled workers and the latest injection molding and die-casting equipment. Our commitment to quality excellence and industry leadership is shown by the fact that we are a council member of the Dongguan City Hardware Machinery Mould Industry Association and hold ISO 9001:2015 certification. Our one-stop service model covers the whole product development cycle, from the initial concept design to mold fabrication, production, and secondary processing. This unified method makes conversation easier, speeds up time-to-market, and makes sure that the design purpose is correctly translated into finished parts. We know that protecting intellectual property is still very important for foreign clients, so we use strict privacy rules and safe data management tools during all stages of a project. Competitive pricing comes from running our business efficiently and being in a good location. We also have strict quality controls that make sure all of our parts meet the high standards for durability and safety in the automotive industry. Being strategically placed near Shenzhen airports makes it easy for international visitors to get to our facility; it's only 20 to 50 minutes from major transportation hubs. Procurement teams are free to come to our facilities, look at our quality systems for themselves, and talk about how our services fit with your needs. During development, our expert team works closely with clients to give advice on materials, ways to improve designs, and the viability of manufacturing. These things improve the performance of parts while keeping costs low. This consultative approach has helped us build long-lasting relationships with buying workers who value low price, dependability, knowledge, and quick support.
Future Trends and Sustainability in Automotive Plastic Components
Environmental Challenges and Circular Economy Solutions
Problems with the environment and solutions for the circular economy
The car industry is under more and more pressure to deal with plastic trash at all stages of a vehicle's life, from making waste to getting rid of parts that are no longer useful. The current system for reusing thermoplastics works pretty well when the parts only contain one type of resin, but mixing materials and contamination make things very hard. Design for recyclability principles encourage choosing materials that are commonly recycled, getting rid of combinations of materials that don't work well together, and labeling parts in a way that makes them easier to sort when taking vehicles apart. Closed-loop recycling systems are ideal because they let manufacturing waste go back into production processes without affecting the quality. We use this method a lot for injection molding runners and discarded parts, turning them into regrind material that is mixed with new plastic in controlled amounts. There are more problems with post-consumer recycling because of pollution, material degradation from service contact, and the collection procedures. However, new sorting technologies and chemical recycling methods show promise for making circular material flows bigger. More and more, procurement specs include requirements for recyclable content. This encourages suppliers to invest in recycling facilities and creates demand for recovered materials in the market.
Advanced Materials and Lightweighting Initiatives
Using bio-based plastic components from natural materials could help us become less reliant on fossil fuels, but the ones we have now often don't work as well or cost more than petroleum-based options. Polylactic acid materials are used in inner parts that aren't solid, and bio-based polyamides made from castor oil can be used instead of regular nylons in some situations. As new materials are made, these choices keep getting better. The next wave of formulas aims for performance balance as well as environmental benefits. Nano-reinforced composites are a growing technology that improves the qualities of plastic by adding small molecules. Carbon nanotubes, graphene platelets, and nano-clays boost strength, heat conductivity, and barrier qualities at very low loading percentages. This means that performance can be improved without adding weight, which is what happens with standard glass fiber reinforcement. Commercial use is still limited by the cost of materials and the difficulty of making them, but special uses in high-performance cars show that the technology can work. Regulatory pressures and business green promises are speeding up efforts to make the automobile industry lighter. Mass reduction is strongly encouraged by fuel economy standards in major markets. The growth of electric vehicles reinforces these drives since the weight of the batteries necessitates weight decreases in other areas. Modern plastic technologies make it easier and easier to replace metal parts. For example, designed thermoplastics or composite materials are now used in structural applications that used to only use steel or aluminum. This trend opens up chances for sellers who put money into learning more about the materials and getting better at handling them.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Adaptation
Instead of focusing only on what they can make now, procurement teams should build relationships with providers who are committed to innovation and technical flexibility. Because materials and handling technologies change so quickly, a supplier's skills today may not be a good indicator of how they will place themselves in the market tomorrow. When suppliers spend money on research relationships, new tools, and training for their employees, they set themselves up to provide next-generation solutions as needs change. Being flexible with standards and open to new ideas is what makes innovation possible. Instead of making strict rules about materials and methods, laying out functional needs and performance standards lets providers use their unique skills to come up with the best solutions. This joint technique often finds ways to cut costs or improve performance that can't be found using traditional methods of design. Building smart relationships with key providers gives both of you a reason to keep getting better and gives you priority access to capacity when supplies are low.
Conclusion
Precision plastic components are now an important part of all modern car systems because they reduce weight, prevent rust, and allow for more design options than traditional materials. To be good at buying, you need to know more than just piece prices about how things are made, how materials work, and how much they will cost altogether. As the industry moves toward more sustainable practices, improved materials, and lighter products, buying workers face both hurdles and possibilities. Automotive companies can handle this changing environment well by working with experienced makers that offer a wide range of skills, tried-and-true quality systems, and joint technical support. This helps them stay ahead of the competition by finding parts more efficiently.
FAQ
What factors should guide material selection for automotive plastic components?
Material selection balances mechanical property requirements, environmental exposure conditions, aesthetic considerations, and cost constraints specific to each application. Under-hood components demand heat resistance and chemical compatibility, while interior parts prioritize surface finish and impact resistance. Glass reinforcement enhances strength and stiffness but affects surface appearance and processing difficulty. Working with experienced suppliers who understand automotive requirements helps identify optimal material choices that meet performance criteria at competitive costs.
What lead times should we expect for custom injection-molded parts?
Typical timelines span 8-12 weeks for mold fabrication, depending on complexity, followed by 2-3 weeks for sampling and refinement iterations. Production lead times vary with order volume and supplier capacity, generally ranging from 3-6 weeks for initial orders. Establishing clear specifications upfront and minimizing design changes during development prevents delays. Experienced suppliers provide realistic schedules accounting for potential iterations rather than optimistic estimates that create downstream problems.
How do we verify components meet automotive safety and durability standards?
Request detailed quality plans documenting inspection procedures, testing protocols, and acceptance criteria for critical characteristics. Supplier certifications like IATF 16949 demonstrate automotive quality system implementation. Component validation should include dimensional verification, material property testing, and functional testing simulating service conditions. Third-party testing laboratories provide independent verification when internal expertise proves limited. Ongoing production monitoring through statistical process control ensures consistent quality across production runs.
Can plastic components truly replace metal parts in structural applications?
Engineered plastics and composites increasingly serve in semi-structural roles where previous generations relied exclusively on metals. Glass-reinforced polyamides deliver sufficient strength for mounting brackets, small housings, and lightly loaded structural elements. Carbon fiber composites approach metal performance in stiffness and strength while reducing weight substantially. Application-specific analysis determines suitability—many scenarios favor plastics when total performance requirements, including corrosion resistance and part consolidation, receive consideration beyond simple strength comparisons.
What intellectual property protections should we expect from manufacturing partners?
Reputable suppliers implement confidentiality agreements before reviewing proprietary designs, maintain secure data management systems, and restrict access to client information on a need-to-know basis. Physical security measures prevent unauthorized mold usage or design disclosure. Contractual provisions should address ownership of tooling, restrictions on selling to competitors, and remedies for IP violations. Geographic considerations affect IP risk, with suppliers in jurisdictions offering robust legal protections and enforcement mechanisms providing greater assurance.
How do we balance cost reduction with quality maintenance in component sourcing?
Focus on the total cost of ownership rather than the piece price alone, accounting for failure costs, warranty exposure, and lifecycle expenses. Value engineering collaborations with suppliers often identify cost reduction opportunities through design optimization, alternative materials, or process improvements that maintain or enhance quality. Consolidating orders with fewer strategic suppliers creates volume leverage while simplifying quality management. Avoid pursuing unsustainably low pricing that compromises supplier viability or incentivizes quality shortcuts with expensive long-term consequences.
Partner with Yongsheng: Your Precision Plastic Components Supplier
Yongsheng brings three decades of specialized expertise in automotive plastic components manufacturing, combining advanced injection molding capabilities with comprehensive design support and rigorous quality systems. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified facility delivers one-stop service from initial concept through production, ensuring your components meet demanding performance requirements while maintaining cost competitiveness. We protect intellectual property through strict confidentiality protocols and serve as a reliable plastic components manufacturer for procurement teams seeking a trusted Chinese partner. Contact our team at sales@alwinasia.com to discuss your specific requirements, request technical consultation, or schedule a facility visit. We deliver the quality, reliability, and responsive support your automotive projects demand.
References
1. Society of Automotive Engineers International, "Plastic and Polymer Composites in Light Vehicles: Materials Selection and Applications," SAE Technical Paper Series, 2022.
2. American Chemistry Council, "Plastics and Polymer Composites in Automotive Markets: Performance Benefits and Sustainability Considerations," Plastics Division Industry Report, 2021.
3. Goodship, V. and Jacobs, D., "Injection Molding of Engineering Plastics for Automotive Applications: Process Optimization and Quality Control," Hanser Publications, 2023.
4. International Organization for Standardization, "Quality Management Systems: Requirements for Automotive Production and Service Parts Organizations - ISO/TS 16949 Implementation Guide," ISO Standards Catalogue, 2020.
5. Friedrich, K. and Almajid, A.A., "Manufacturing Aspects of Advanced Polymer Composites for Automotive Applications: Recent Developments and Future Trends," Applied Composite Materials Journal, Volume 29, 2022.
6. European Automobile Manufacturers Association, "Circular Economy and Recycling of Automotive Plastics: Industry Practices and Future Directions," ACEA Position Paper on Sustainability, 2023.

We can provide a one-stop service, including design and development, mold fabrication, production, product processing, etc.

Professional injection mold, die casting mold, plastic products OEM manufacturer